The battle for dominance in artificial intelligence and cloud services has intensified as Google and Microsoft continue to innovate and expand their offerings. Both tech giants have made significant investments in these technologies, recognizing them as critical drivers of future growth. This comprehensive comparison examines how these industry leaders stack up against each other across key dimensions, from technological capabilities to market positioning, helping organizations make informed decisions about which platform might best serve their needs.
Company Overview and Strategic Vision
Google’s journey into cloud computing began in 2008 with the launch of App Engine, which later evolved into Google Cloud Platform (GCP) in 2012. The company’s strategic vision has been shaped by its data-centric approach, leveraging its massive infrastructure originally built to power its search engine and other consumer services. In 2016, Google formalized its commitment to an “AI-first” strategy, integrating artificial intelligence across its product portfolio.
Microsoft’s cloud evolution started with Azure’s launch in 2010, building upon decades of enterprise software experience. Under CEO Satya Nadella’s leadership since 2014, Microsoft pivoted to an “intelligent cloud, intelligent edge” vision, emphasizing the integration of cloud services with AI capabilities. This strategic shift represented a fundamental transformation for the company, moving from its traditional software licensing model to cloud-based services.
While Google approaches AI and cloud from its background in consumer services and data processing at scale, Microsoft leverages its deep enterprise relationships and productivity ecosystem. These different starting points have influenced how each company has developed and positioned their offerings in the market.
Core Focus and Technological Edge
Google’s Data-Driven Approach
Google’s technological edge stems from its pioneering work in large-scale data processing and machine learning. The company has developed and open-sourced influential frameworks like TensorFlow, which has become one of the most widely used machine learning libraries globally. Google’s infrastructure was built to handle enormous data volumes efficiently, giving it natural advantages in big data analytics and machine learning workloads.
The company’s focus on open-source technologies extends beyond TensorFlow to Kubernetes, which has become the industry standard for container orchestration. This commitment to open-source has helped Google build goodwill within developer communities while ensuring its technologies gain widespread adoption.
Microsoft’s Enterprise Integration
Microsoft’s core strength lies in its comprehensive enterprise ecosystem and the seamless integration between its productivity tools and cloud services. The company has leveraged its dominant position with Office 365, Teams, and Windows to create natural pathways for businesses to adopt Azure services.
Microsoft’s acquisition of GitHub in 2018 and its strategic partnership with OpenAI have further strengthened its position in developer tools and cutting-edge AI. The company has focused on creating practical AI applications that integrate directly into business workflows, as evidenced by its Copilot offerings across Microsoft 365 applications.
Strengths and Weaknesses
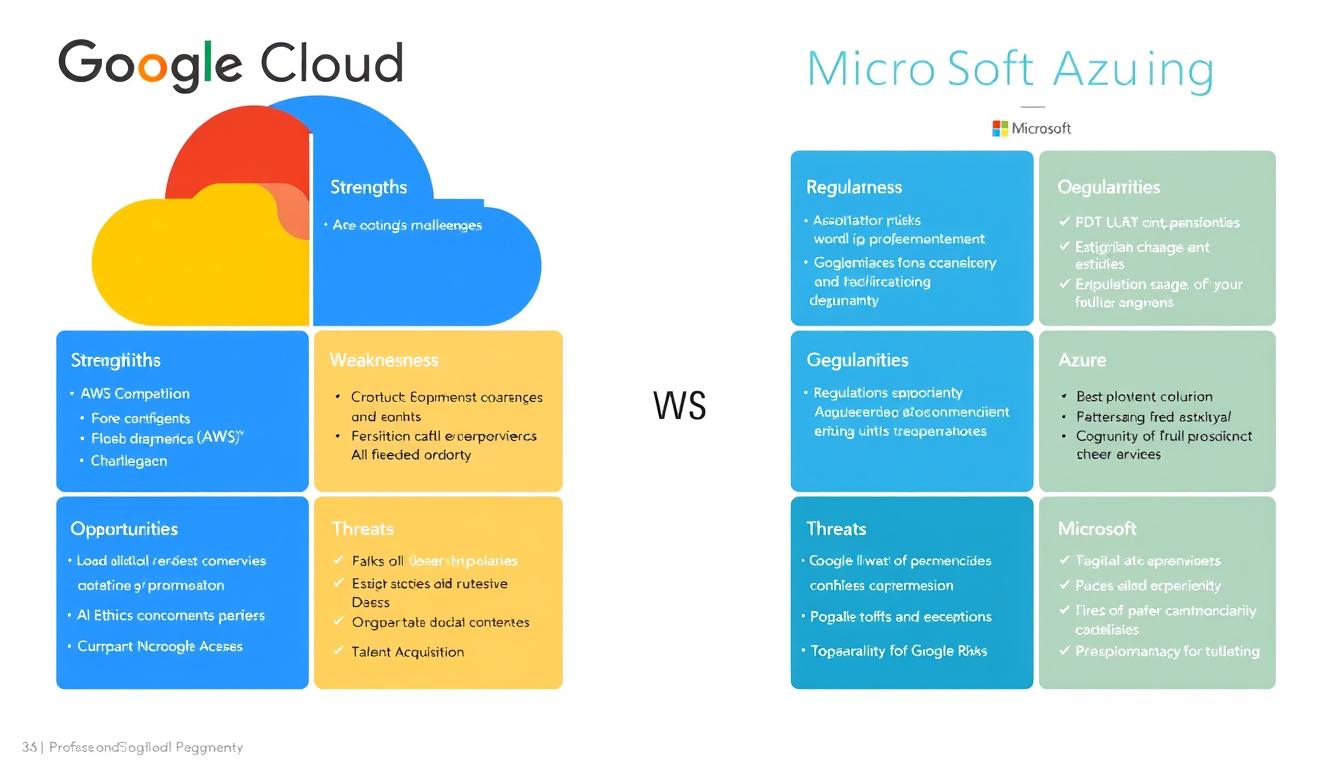
Google Cloud Strengths
- Superior data analytics capabilities with BigQuery
- Industry-leading machine learning infrastructure
- Strong open-source community engagement
- Advanced networking with global private fiber network
- Cutting-edge AI research translated into practical services
Google Cloud Weaknesses
- Smaller enterprise customer base compared to competitors
- Less comprehensive enterprise support infrastructure
- Fewer global regions than Azure
- Perception of commitment issues with product longevity
- Less integrated enterprise productivity ecosystem
Microsoft Azure Strengths
- Seamless integration with Microsoft 365 ecosystem
- Extensive global datacenter presence
- Strong hybrid cloud capabilities with Azure Stack
- Comprehensive enterprise security and compliance
- Deep enterprise relationships and understanding
Microsoft Azure Weaknesses
- More complex pricing structure
- Less optimized for container-native workloads
- Steeper learning curve for non-Microsoft developers
- Less advanced in open-source technologies
- Higher costs for certain workloads compared to GCP
Both platforms have distinct architectural approaches to cloud infrastructure. Google Cloud’s infrastructure was built from the ground up for cloud-native applications, giving it advantages in containerization and serverless computing. This architecture allows developers to leverage microservices effectively, facilitating rapid deployment and scalability.
Google Cloud also offers Kubernetes, a leading orchestration platform for managing containerized applications, which further enhances its appeal for modern development practices. Microsoft Azure, meanwhile, has focused on creating bridges between traditional enterprise workloads and modern cloud architectures, making it particularly strong in hybrid scenarios.
This hybrid capability enables organizations to seamlessly integrate on-premises resources with cloud services, allowing for greater flexibility and control over their IT environments. Azure’s robust support for various programming languages and frameworks also makes it a versatile choice for enterprises transitioning to the cloud.
Innovation and Product Portfolio
AI Breakthroughs
Google’s AI portfolio is headlined by Gemini, its most capable multimodal AI model that powers various services including Vertex AI. Google’s AI research arm, Google DeepMind (following the merger with DeepMind), continues to produce groundbreaking research in reinforcement learning and multimodal AI. The company’s AI innovations are deployed across its cloud offerings, with particular strength in natural language processing, computer vision, and recommendation systems.
Microsoft has taken a different approach, focusing on commercializing AI through strategic partnerships, most notably with OpenAI. This relationship has allowed Microsoft to rapidly integrate advanced AI capabilities into its products through services like Azure OpenAI Service and the Copilot suite of AI assistants. Microsoft has effectively embedded AI into its productivity tools, creating practical applications that enhance everyday business workflows.
Cloud Services Comparison
| Service Category | Google Cloud | Microsoft Azure |
| Data Analytics | BigQuery, Dataflow, Pub/Sub | Synapse Analytics, Data Factory, Event Hubs |
| AI/ML Platform | Vertex AI, TensorFlow, AutoML | Azure Machine Learning, Azure OpenAI Service |
| Compute | Compute Engine, GKE, Cloud Run | Virtual Machines, AKS, Container Apps |
| Storage | Cloud Storage, Filestore, Bigtable | Blob Storage, Files, Cosmos DB |
| Databases | Cloud SQL, Spanner, Firestore | Azure SQL, Cosmos DB, MySQL |
| Serverless | Cloud Functions, Cloud Run | Azure Functions, Logic Apps |
Google Cloud excels in data analytics and machine learning infrastructure, with BigQuery standing out as a particularly powerful tool for large-scale data analysis. Microsoft Azure offers more comprehensive enterprise integration capabilities and a broader range of services tailored to business applications, particularly in hybrid cloud scenarios.
Sustainability and Corporate Responsibility

Both Google and Microsoft have made ambitious commitments to sustainability, recognizing the significant environmental impact of data centers and AI computing.
Carbon Footprint and Renewable Energy
Google has been carbon neutral since 2007 and aims to operate on 24/7 carbon-free energy across all its data centers by 2030. The company has pioneered the use of advanced cooling technologies and AI to optimize data center efficiency. In 2023, Google reported that 66% of its global electricity consumption came from carbon-free sources.
Microsoft has committed to being carbon negative by 2030 and by 2050 aims to remove all the carbon it has emitted since its founding in 1975. The company is also working toward 100% renewable energy for its data centers by 2025. Microsoft has introduced a novel approach with its Sustainability Calculator, which helps Azure customers measure and reduce their carbon emissions.
AI Ethics and Responsible AI
Google published its AI Principles in 2018, establishing guidelines for the responsible development and deployment of AI. The company has implemented governance structures including an Advanced Technology Review Council to evaluate sensitive AI applications. Google’s approach emphasizes fairness, interpretability, privacy, and security.
Microsoft’s Responsible AI Standard provides a framework for building AI systems with human-centered design principles. The company has established an Office of Responsible AI and an AI, Ethics, and Effects in Engineering and Research (AETHER) Committee to govern its AI development. Microsoft has been particularly vocal about the need for AI regulation, calling for thoughtful government oversight of AI technologies.
Financial Performance and Investment
Financial performance provides crucial insights into the momentum and market position of both cloud providers.
Revenue and Growth
Google Cloud generated $29.6 billion in revenue for fiscal year 2023, representing a 26% year-over-year growth. After years of operating losses, Google Cloud achieved profitability in 2023, marking a significant milestone in its maturation as a business. The segment now accounts for approximately 10% of Alphabet’s total revenue.
Microsoft’s Intelligent Cloud segment, which includes Azure and other cloud services, reported $87.9 billion in revenue for fiscal year 2023, growing 22% year-over-year. Azure specifically grew at 30%, outpacing the overall cloud segment. Cloud services now represent Microsoft’s largest business segment, underscoring the company’s successful transformation to a cloud-first organization.
R&D and Capital Expenditure
Both companies have made massive investments in infrastructure and research to support their AI and cloud ambitions. Google’s parent company Alphabet reported $43.5 billion in R&D spending for 2023, with a significant portion directed toward AI and cloud technologies. Capital expenditures reached $31.5 billion, primarily for data center expansion and technical infrastructure.
Microsoft invested $27.2 billion in R&D during fiscal year 2023 and reported $28.1 billion in capital expenditures, with the majority allocated to expanding its global data center footprint and enhancing its AI capabilities. The company has also made strategic investments in partners like OpenAI, reportedly totaling over $13 billion.
These substantial investments reflect both companies’ recognition of AI and cloud as critical to their future growth and competitive positioning. Microsoft’s higher cloud revenue and profitability give it greater financial resources to invest in expansion, while Google’s parent Alphabet maintains a stronger overall cash position, providing flexibility for long-term strategic investments.
Brand Positioning and Public Perception
Developer Sentiment
According to Stack Overflow’s 2023 Developer Survey, Google Cloud Platform is viewed favorably among developers for its technical capabilities, particularly in machine learning and data analytics. Developers appreciate GCP’s clean interface, consistent API design, and comprehensive documentation. Google’s contributions to open-source technologies like Kubernetes and TensorFlow have also built significant goodwill within developer communities.
Microsoft Azure receives high marks for its integration with existing Microsoft tools and enterprise systems. The platform’s broad range of services and strong support for hybrid deployments make it particularly appealing to enterprise developers. Microsoft’s developer-friendly CEO Satya Nadella has successfully repositioned the company as an open and collaborative technology partner, moving away from its earlier reputation for closed ecosystems.
Enterprise Trust and Perception
Microsoft enjoys stronger trust among enterprise decision-makers, leveraging decades of business relationships and its comprehensive compliance and security capabilities. According to Gartner’s 2023 Magic Quadrant for Cloud Infrastructure and Platform Services, Microsoft Azure is positioned as a leader with particularly strong marks for its completeness of vision and ability to execute.
Google Cloud has worked to overcome perceptions about its commitment to enterprise services, with CEO Thomas Kurian (who joined from Oracle in 2019) bringing a stronger enterprise focus. The company has made significant strides in addressing concerns about product longevity and support, though some enterprises still express hesitation about Google’s long-term commitment to certain services given the company’s history of product discontinuations in its consumer business.
“Microsoft has successfully leveraged its enterprise relationships to position Azure as a natural extension of existing investments, while Google Cloud has differentiated through technical excellence and data-centric capabilities.”
Global Partnerships and Ecosystem Development
Strategic Technology Alliances
Google Cloud has formed strategic partnerships with companies like NVIDIA for AI infrastructure, SAP for enterprise applications, and Salesforce for CRM integration. The company has also established the Google Cloud Ready program to certify third-party solutions that integrate seamlessly with its platform. In the open-source space, Google maintains influential positions in foundations governing Kubernetes, TensorFlow, and other key technologies.
Microsoft’s most notable partnership is with OpenAI, which has given it privileged access to cutting-edge AI models like GPT-4 and DALL-E. The company has also strengthened its position through strategic alliances with Oracle (for database interoperability), Adobe (for creative and marketing cloud integration), and SAP (for enterprise resource planning). Microsoft’s extensive partner network includes over 400,000 organizations globally, providing significant reach for its cloud services.
Academic and Research Collaborations
Both companies have established extensive academic programs to nurture the next generation of cloud and AI talent. Google Cloud’s research partnerships include collaborations with institutions like Carnegie Mellon University, MIT, and Stanford, focusing on areas such as quantum computing, machine learning, and sustainability. The company’s TensorFlow Research Cloud provides free computational resources to researchers advancing the field of machine learning.
Microsoft Research maintains one of the largest corporate research organizations, with labs around the world collaborating with academic institutions. The company’s Azure for Research program provides cloud credits and technical support to academic researchers, while its AI for Earth, AI for Health, and AI for Accessibility initiatives support applications of AI to address societal challenges.
These ecosystem development efforts are crucial for both companies as they seek to expand their influence and ensure a pipeline of talent familiar with their platforms. Microsoft’s longer history in enterprise software gives it advantages in business partnerships, while Google’s strong position in the open-source community and academic research provides different kinds of ecosystem benefits.
Challenges and Strategic Risks
Competitive Landscape
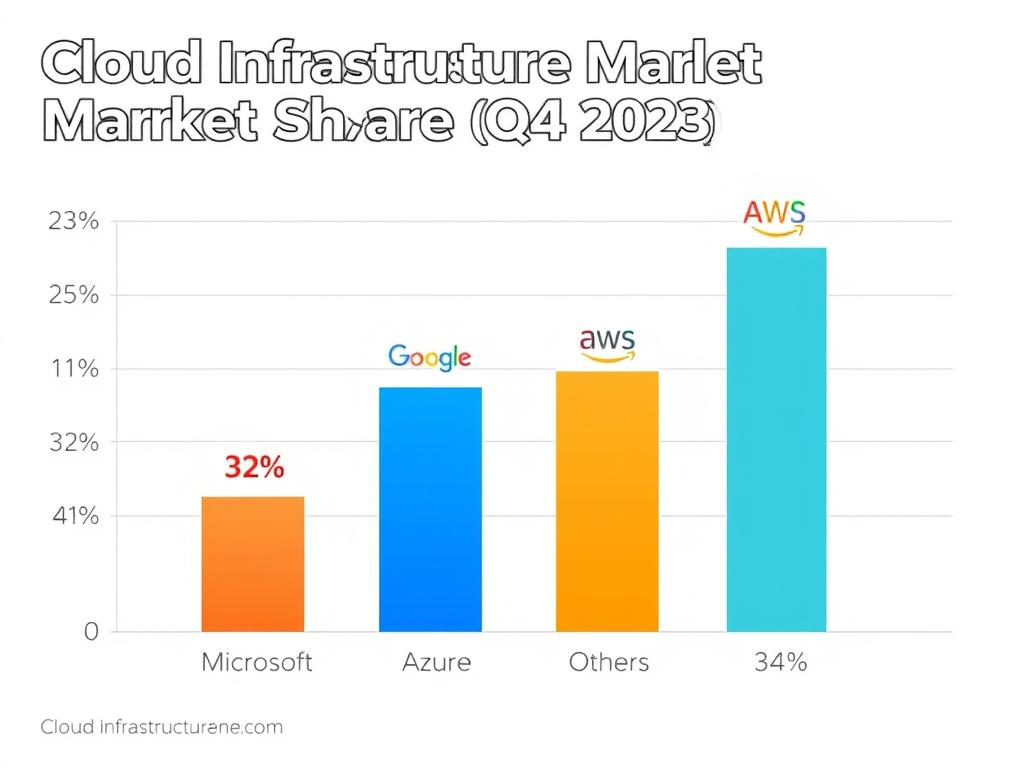
Both Google and Microsoft face intense competition from Amazon Web Services, which maintains its position as the market leader with 32% market share. AWS’s first-mover advantage and extensive service portfolio present ongoing challenges for both companies. Additionally, specialized providers like Snowflake in data warehousing and Databricks in data analytics compete directly with specific high-value services offered by both cloud providers.
Chinese cloud providers like Alibaba Cloud and Tencent Cloud are also expanding globally, particularly in Asia-Pacific markets, creating additional competitive pressure. These providers often have advantages in serving Chinese companies expanding internationally and can leverage lower operating costs in certain regions.
Regulatory and Geopolitical Risks
Both companies face increasing regulatory scrutiny around AI ethics, data sovereignty, and market power. The EU’s Digital Markets Act and AI Act impose significant compliance requirements, while countries like China, Russia, and India have implemented data localization laws that complicate global cloud operations. Antitrust investigations in various jurisdictions could potentially limit acquisition strategies or force changes to platform policies.
Geopolitical tensions also create challenges for global cloud operations, with increasing fragmentation of technology standards and regulatory regimes. Both Google and Microsoft must navigate complex international relationships while maintaining consistent global service offerings.
Technical and Operational Challenges
The rapid pace of AI advancement creates challenges in maintaining state-of-the-art offerings while ensuring reliability, security, and ethical use. Both companies face significant technical hurdles in scaling AI infrastructure efficiently, particularly as models grow larger and more computationally intensive. The global chip shortage and supply chain disruptions have also impacted data center expansion plans.
Talent acquisition remains a critical challenge, with intense competition for AI researchers, cloud architects, and security specialists. Both companies have responded with aggressive compensation packages and acquisition of AI startups to secure top talent.
How are Google and Microsoft addressing AI safety concerns?
Both companies have established internal ethics committees and governance structures to evaluate AI applications. Google’s AI Principles and Microsoft’s Responsible AI Standard provide frameworks for development, while both companies invest in technical research on explainability, fairness, and safety. Microsoft has been particularly vocal in advocating for government regulation of advanced AI systems, while Google has emphasized the importance of open research and multi-stakeholder governance approaches.
Conclusion: Choosing Between Google Cloud and Microsoft Azure
The choice between Google Cloud and Microsoft Azure ultimately depends on an organization’s specific needs, existing technology investments, and strategic priorities. Organizations heavily invested in Microsoft’s productivity ecosystem may find Azure offers more seamless integration and familiar administrative tools. Conversely, companies with advanced data analytics requirements or those building AI-intensive applications might find Google Cloud’s technical capabilities more aligned with their needs.
Many enterprises are adopting multi-cloud strategies, using different providers for different workloads based on their respective strengths. This approach can mitigate vendor lock-in risks while allowing organizations to leverage the best capabilities from each platform.
Both Google and Microsoft continue to invest heavily in their cloud and AI capabilities, with the competitive landscape evolving rapidly. Microsoft’s enterprise relationships and integrated productivity tools give it advantages in business adoption, while Google’s technical innovation and data-centric approach provide differentiated capabilities for specific use cases.
As AI becomes increasingly central to cloud services, both companies are positioning themselves for the next wave of innovation. The race between Google and Microsoft in artificial intelligence and cloud services represents not just a competition for market share, but a fundamental contest to shape the future of computing.