The ride-hailing industry has transformed urban mobility worldwide, with Uber and Careem emerging as dominant forces in their respective markets. While Uber built its empire from San Francisco to become a global phenomenon, Careem developed a strong regional presence across the Middle East and North Africa before being acquired by Uber in 2020. This comprehensive analysis examines how these mobility giants compare across ten critical dimensions, from their founding stories to future visions, providing valuable insights for industry observers, potential investors, and mobility ecosystem participants.
Company Background and Market Position
Uber and Careem represent two different approaches to the ride-hailing market. Founded in 2009 by Travis Kalanick and Garrett Camp, Uber pioneered the modern ride-hailing concept in San Francisco before expanding globally. The company went public in 2019 with one of the largest IPOs in tech history, despite not yet achieving consistent profitability at the time.
Careem, established in 2012 by Mudassir Sheikha and Magnus Olsson, began as a corporate car booking service in Dubai before evolving into a comprehensive mobility platform across the Middle East, North Africa, and South Asia. Uber’s acquisition of Careem for $3.1 billion in 2020 marked a significant consolidation in the industry while allowing Careem to maintain operational independence.
Uber’s Global Approach
Uber’s mission of “transportation as reliable as running water, everywhere for everyone” reflects its global ambitions. The company operates in over 70 countries and 10,500+ cities worldwide, with a standardized approach that maintains consistent branding and user experience across markets, with limited localization.
Careem’s Regional Focus
Careem’s mission to “simplify and improve lives” in the Middle East region has guided its development as a super-app tailored to local needs. Operating in 100+ cities across 13 countries, Careem emphasizes deep cultural integration and hyperlocal services that address specific regional challenges.
Core Focus and Service Offerings
Both companies have expanded beyond basic ride-hailing to create comprehensive mobility ecosystems, though with different approaches to service diversification.

| Service Category | Uber | Careem |
| Ride-hailing | UberX, Uber Black, Uber Comfort, UberXL, Uber Green | Careem GO, Careem Business, Careem MAX, Careem Economy |
| Food Delivery | Uber Eats (global platform with 500,000+ restaurants) | Careem NOW (focused on MENA region with local cuisine options) |
| Micro-mobility | JUMP bikes and scooters (available in select cities) | Careem Bike (primarily in UAE and select MENA cities) |
| Payment Solutions | Uber Cash (digital wallet for Uber ecosystem) | Careem Pay (broader financial services including bill payments) |
| Grocery/Shopping | Uber Grocery (partnership with local stores) | Careem Shops (integrated shopping experience) |
| Public Transit Integration | Uber Transit (journey planning with public options) | Careem Bus (dedicated bus service in select markets) |
While Uber maintains a broader global footprint with standardized services, Careem has developed a super-app approach more tailored to MENA region needs, including services like bill payments and cleaning services that address specific local pain points.
Strengths and Weaknesses Analysis
Uber Strengths
- Global brand recognition and presence in 70+ countries
- Diversified revenue streams across multiple service categories
- Strong technology infrastructure with significant R&D investment
- Public company status providing access to capital markets
- Economies of scale allowing competitive pricing in mature markets
Uber Weaknesses
- Regulatory challenges in multiple markets affecting operations
- Driver satisfaction issues and high turnover in competitive markets
- Standardized approach limiting cultural adaptation in some regions
- Profitability concerns in certain markets and service categories
- Public scrutiny and brand reputation challenges in some regions
Careem Strengths
- Deep regional expertise and cultural alignment in MENA markets
- Super-app strategy creating stronger user retention and frequency
- Localized payment solutions including cash options in relevant markets
- Strong brand loyalty in core markets with cultural relevance
- Operational autonomy despite Uber acquisition
Careem Weaknesses
- Limited global expansion potential compared to Uber
- Smaller user base restricting network effects in some services
- Regional economic and political instability in some markets
- Resource constraints for technology development compared to Uber
- Potential long-term autonomy concerns following acquisition
Innovation and Technology
Both companies leverage advanced technology to optimize their operations, though with different focuses and implementation approaches.
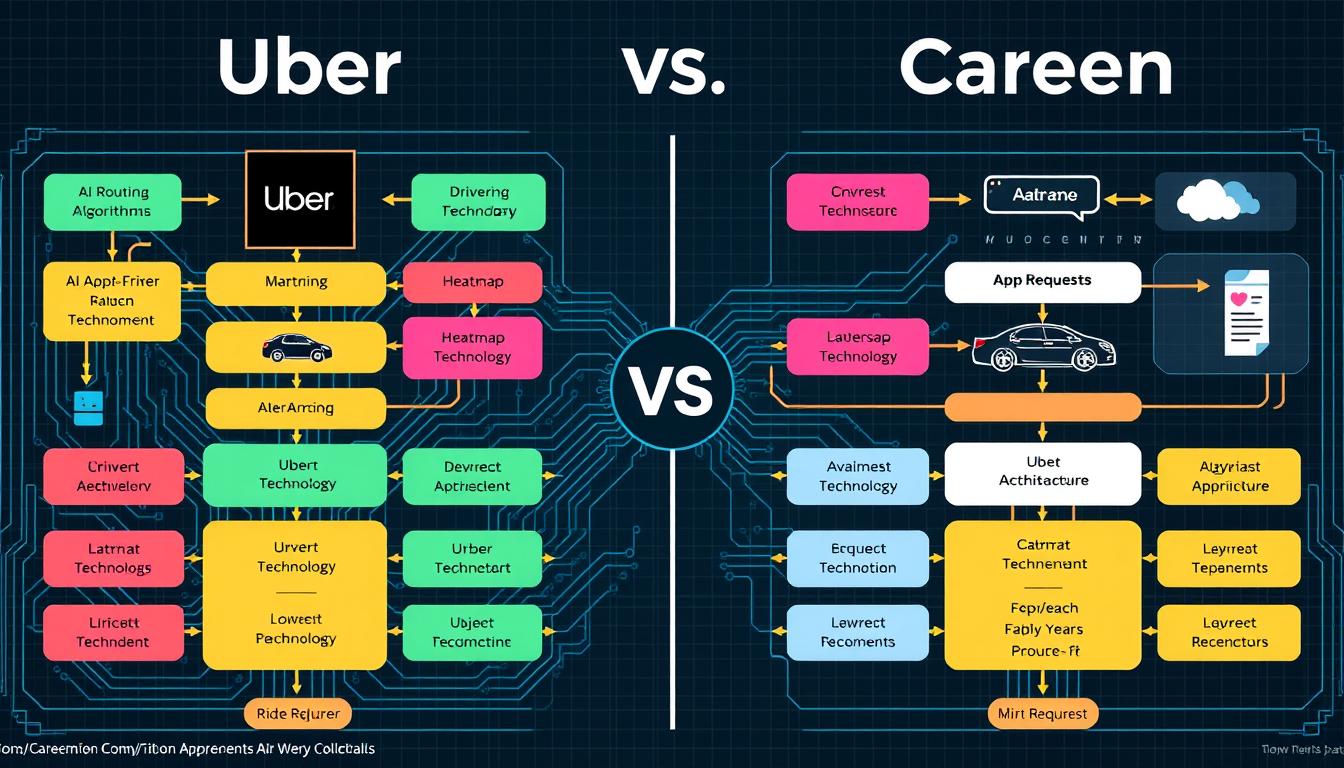
| Technology Area | Uber Approach | Careem Approach |
| Routing Algorithms | Uber Forecasting uses machine learning to predict demand patterns and optimize driver positioning | Captain AI optimizes routes based on local traffic patterns and regional driving behaviors |
| Matching Systems | Global matching algorithm with standardized parameters across markets | Localized matching considering regional preferences like gender matching in conservative markets |
| Heatmap Technology | Dynamic surge pricing based on real-time demand across all markets | Market-specific surge models accounting for local events and regional patterns |
| Public Transit Integration | Uber Transit offers journey planning with public options in select cities | Careem Bus provides dedicated bus service tailored to regional commuting patterns |
| Payment Processing | Digital-first approach with credit card emphasis | Hybrid system supporting cash payments and digital options |
Uber’s technology development benefits from greater resources and global data collection, while Careem focuses on solving specific regional challenges with targeted innovations. Both companies continue to invest in AI and machine learning to improve efficiency and user experience.
Sustainability and Green Initiatives
As transportation contributes significantly to global emissions, both Uber and Careem have developed sustainability strategies, though with different timelines and approaches.
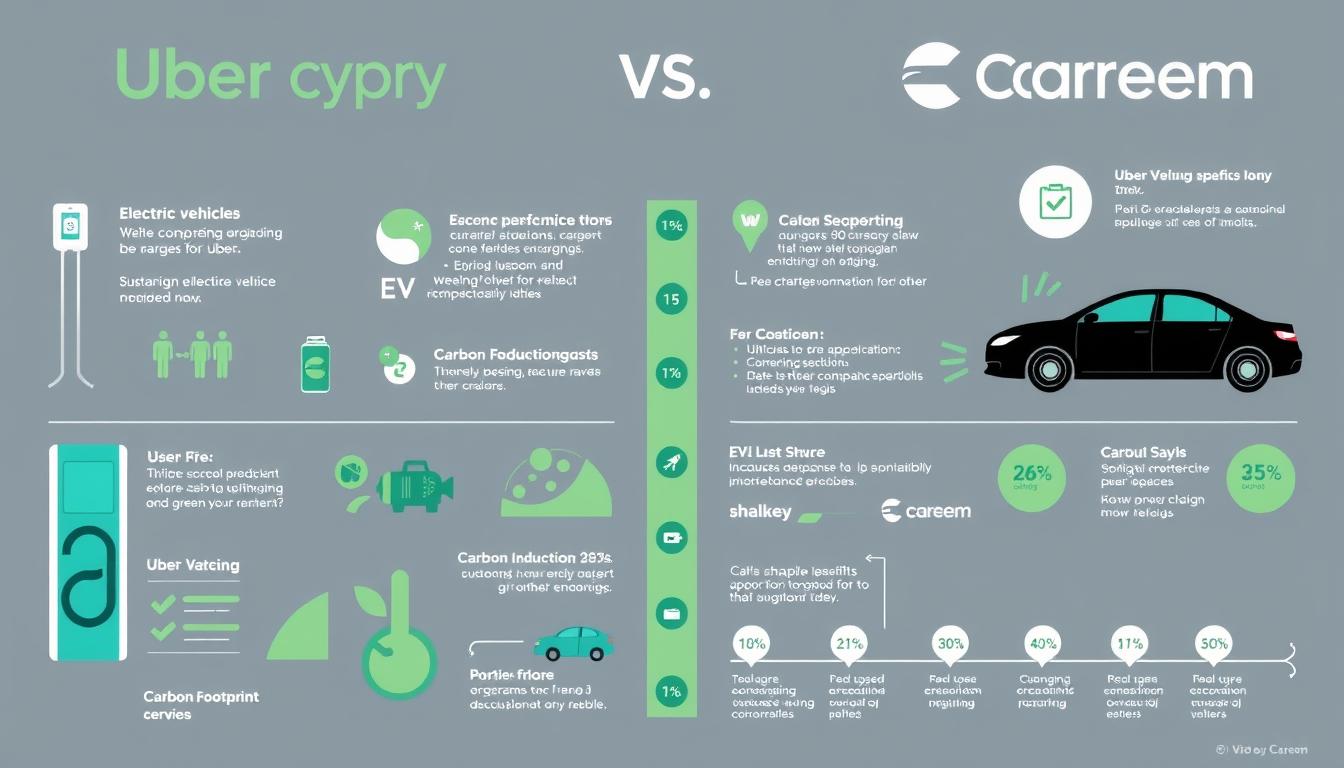
Uber’s Global Green Strategy
Uber has committed to becoming a fully zero-emission platform by 2040, with 100% of rides taking place in zero-emission vehicles, on public transit, or with micromobility options. The company has pledged $800 million to help drivers transition to electric vehicles and has launched Uber Green in 1,400+ cities globally.
Careem’s Regional Approach
Careem has focused on market-specific sustainability initiatives, including partnerships with electric vehicle providers in the UAE and Saudi Arabia. The company has introduced Careem Bike in Dubai and Abu Dhabi as an eco-friendly alternative and has begun integrating hybrid and electric vehicles into its fleet in select markets.
While Uber has made more public commitments with specific targets and timelines, Careem’s approach reflects the varying infrastructure readiness across its markets. Both companies recognize the importance of sustainability for long-term business viability and customer perception.
Financial Performance and Growth
The financial trajectories of Uber and Careem reflect their different scales, market positions, and business strategies.
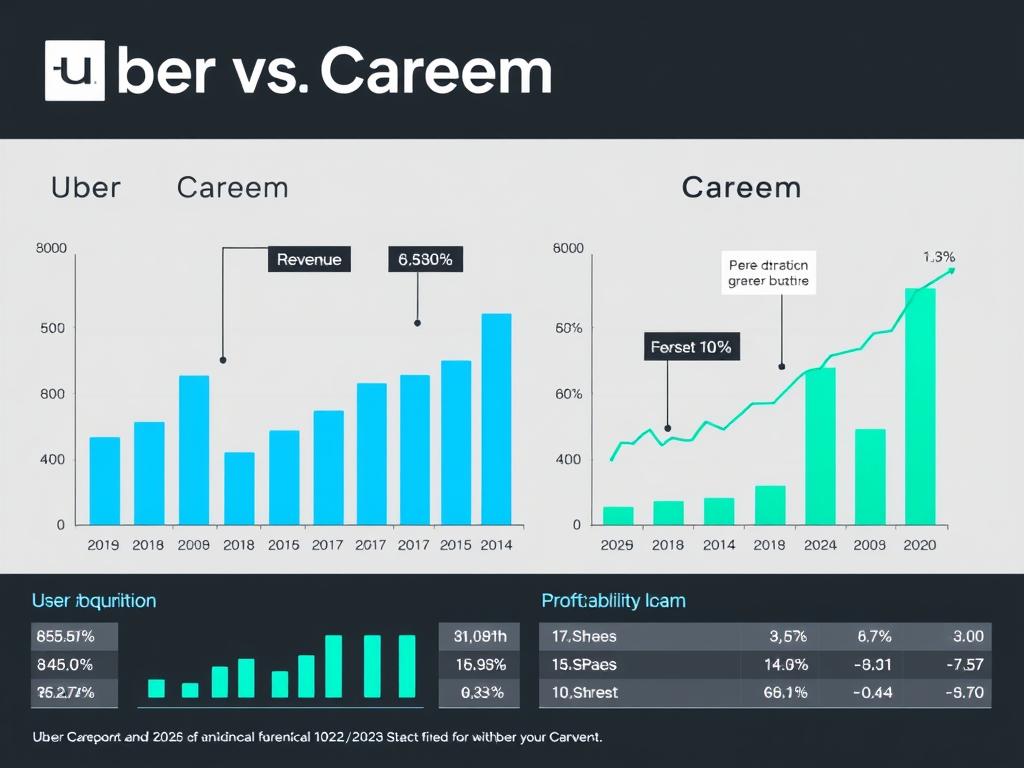
| Financial Metric | Uber (2023) | Careem (Post-Acquisition) |
| Revenue | $37.3 billion | Not publicly disclosed (operates as subsidiary) |
| Gross Bookings | $138.5 billion | Estimated $2-3 billion (regional focus) |
| Profitability | First profitable year on adjusted EBITDA basis | Profitability varies by market; super-app strategy driving growth |
| Growth Strategy | Global expansion and service diversification | Regional deepening and super-app ecosystem development |
| Investment Focus | Technology platform, autonomous vehicles, global markets | Regional service expansion, payment infrastructure, local partnerships |
Uber’s scale provides significant advantages in terms of investment capacity and global reach, while Careem’s focused regional approach allows for deeper market penetration and service customization in its core territories. The acquisition has created a complex relationship where Careem maintains operational independence while benefiting from Uber’s resources.
Brand Trust and User Experience
User trust and experience are critical factors in the ride-hailing industry, with both companies implementing various approaches to build loyalty and ensure safety.
Careem’s localized approach tends to result in higher customer satisfaction in MENA markets, with support options tailored to regional preferences. Uber’s global consistency provides reliability across markets but sometimes lacks cultural nuance. Both companies have invested significantly in safety features, though implementation varies by region based on local regulations and user expectations.
Global and Local Impact
The contrasting approaches of Uber and Careem highlight different strategies for market penetration and adaptation.
Uber’s Standardization
Uber’s approach emphasizes consistent global branding and user experience, with limited market-specific adaptations. This standardization creates efficiency and brand recognition but can limit effectiveness in markets with unique needs. The company’s scale allows it to influence transportation policy globally and set industry standards.
Careem’s Localization
Careem’s hyperlocal strategy includes market-specific features like cash payments in Egypt, female drivers for female passengers in conservative markets, and call centers for users less comfortable with app-only support. This approach has created stronger brand loyalty in MENA markets but limits global scalability.
The different approaches reflect each company’s origins and strategic priorities. Uber’s global scale provides advantages in technology development and standardization, while Careem’s regional focus enables deeper market penetration and cultural alignment in specific countries.
Challenges and Future Vision
Both Uber and Careem face significant challenges as they navigate evolving regulatory landscapes and emerging technologies.
What regulatory challenges do Uber and Careem face?
Both companies navigate complex regulatory environments that vary by market. Uber faces driver classification battles in the EU and US, with courts increasingly ruling that drivers should be classified as employees rather than independent contractors. Careem deals with licensing fees in Saudi Arabia and operational restrictions in markets like Egypt and Jordan. Both must adapt to evolving data privacy regulations and transportation-specific legislation.
How are they approaching autonomous vehicle technology?
Uber has restructured its autonomous vehicle strategy after selling its Advanced Technologies Group to Aurora in 2020, now focusing on partnerships rather than in-house development. Careem has explored autonomous technology through partnerships in the UAE, though at a smaller scale. Both companies view autonomy as a long-term evolution of their platforms rather than an immediate transformation.
What does the future of the super-app strategy look like?
Careem has embraced the super-app model more aggressively, integrating diverse services from food delivery to bill payments within a single application. Uber has moved in this direction more cautiously in global markets, though its acquisition of Postmates and integration of Uber Eats indicates similar ambitions. The success of these strategies depends on regional user preferences and competitive dynamics.
The future of both companies will be shaped by their ability to navigate regulatory challenges, adapt to technological changes, and maintain competitive advantages in their respective markets. Uber’s global scale provides resources for innovation, while Careem’s regional expertise enables nimble adaptation to local market shifts.
Conclusion: Different Paths to Mobility Leadership
The Uber vs Careem comparison reveals two distinct approaches to building mobility platforms. Uber’s global standardization strategy has created a consistent worldwide brand but sometimes struggles with local adaptation. Careem’s regional focus and cultural integration have built strong loyalty in MENA markets but limited its global expansion potential.
Both companies excel in different aspects of mobility services. Uber leads in global scale, technology resources, and service diversity across markets. Careem dominates in regional expertise, cultural alignment, and super-app integration in the MENA region. The 2020 acquisition created a complex relationship where both entities continue to operate with distinct strategies while sharing technology and resources.
For industry observers, investors, and mobility ecosystem participants, understanding these different approaches provides valuable insights into regional market dynamics and the evolution of transportation platforms. As urban mobility continues to transform, both companies will play significant roles in shaping how people move, eat, and access services in cities worldwide.