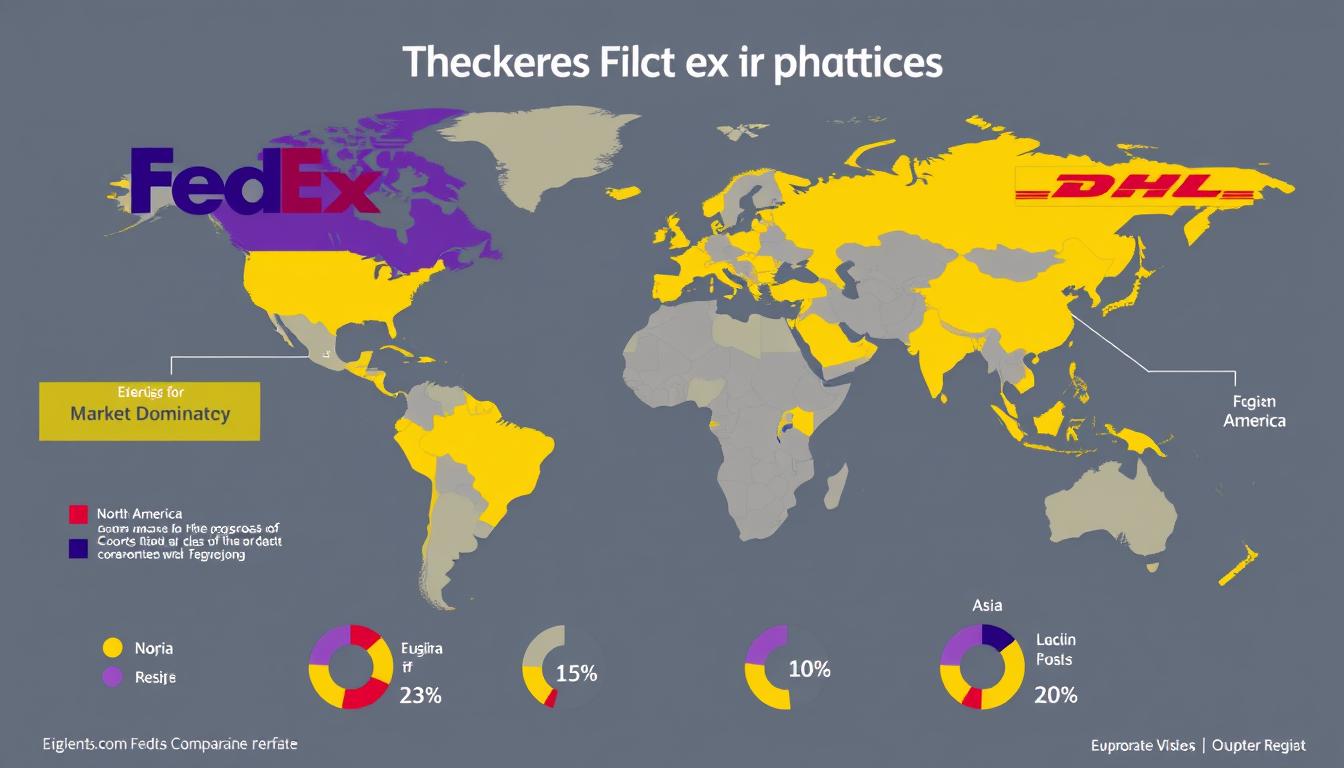
In today’s fast-paced global marketplace, shipping speed can make or break business operations. Whether you’re managing a supply chain, overseeing logistics, or making strategic decisions about shipping partners, the difference between same-day delivery and next-day arrival can significantly impact customer satisfaction and operational efficiency. FedEx and DHL stand as titans in the global logistics industry, each claiming to offer superior shipping services with unmatched speed and reliability.
But which carrier truly delivers faster? This comprehensive analysis examines FedEx and DHL across ten critical performance dimensions, focusing specifically on speed, efficiency, and innovation in global logistics. By analyzing their operational capabilities, technological infrastructure, and performance metrics, we’ll provide you with the data-driven insights needed to determine which shipping giant better meets your specific business requirements.
Company Origins and Global Mission
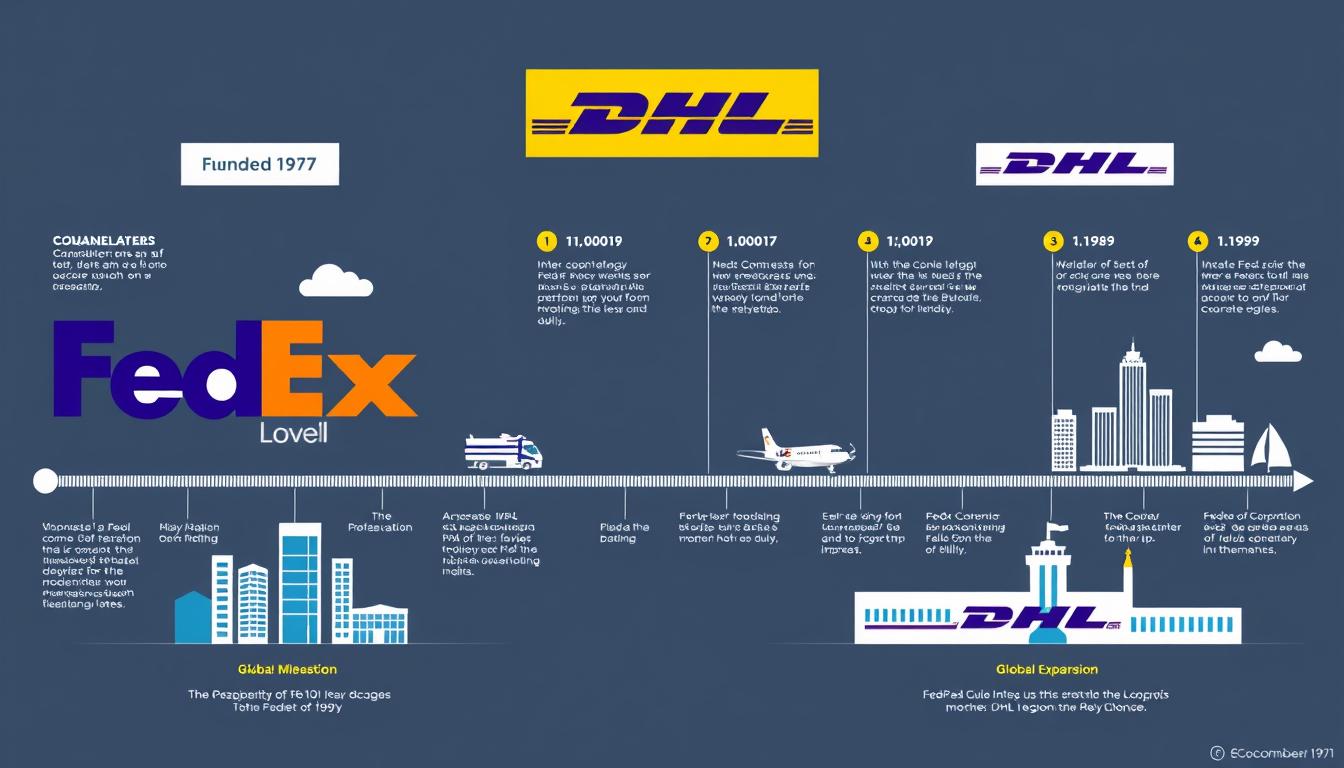
FedEx, originally Federal Express, was founded in 1971 by Frederick W. Smith with a revolutionary business model centered on overnight delivery. Smith’s vision was encapsulated in the company’s enduring mission: “The World On Time.” Starting with just 14 small aircraft serving 25 U.S. cities, FedEx pioneered the hub-and-spoke distribution system that revolutionized the shipping industry. This innovation allowed packages to be efficiently routed through a central hub, dramatically reducing delivery times.
DHL, founded slightly earlier in 1969 by Adrian Dalsey, Larry Hillblom, and Robert Lynn (hence the name DHL), began by offering document delivery services between San Francisco and Honolulu. The company’s mission, “Excellence. Simply Delivered,” reflects its commitment to straightforward, efficient service. DHL’s early focus on international shipping, particularly to markets underserved by competitors, established its global footprint before expanding into comprehensive logistics solutions.
Both companies have evolved significantly over the decades. FedEx has grown through strategic acquisitions like Flying Tigers (1989) and TNT Express (2016), expanding its global reach while maintaining its core focus on speed. DHL became part of Deutsche Post in 2002, strengthening its European operations while continuing to expand its international network. Today, both companies’ missions directly influence their approach to shipping speed, with FedEx emphasizing time-definite delivery and DHL focusing on international expertise and simplified cross-border shipping.
Core Services and Operational Scope
| Service Category | FedEx Offerings | DHL Offerings |
| Express Shipping | FedEx Priority Overnight (next business morning) FedEx Standard Overnight (next business afternoon) FedEx 2Day (2 business days) |
DHL Express 9:00 (by 9:00 AM) DHL Express 12:00 (by noon) DHL Express Worldwide (end of next business day) |
| Same-Day Options | FedEx SameDay FedEx SameDay City |
DHL Same Day Sprintline DHL Same Day Jetline |
| International Express | FedEx International Priority (1-3 business days) FedEx International Economy (2-5 business days) |
DHL Express Worldwide (1-3 business days) DHL Express Economy Select (2-5 business days) |
| Freight Services | FedEx Freight Priority FedEx Freight Economy FedEx International Priority Freight |
DHL Global Forwarding DHL Freight DHL Industrial Projects |
| E-commerce Solutions | FedEx Fulfillment FedEx Cross Border FedEx Returns Technology |
DHL eCommerce DHL Parcel Metro DHL Parcel International Direct |
FedEx and DHL both offer comprehensive shipping services, but with distinct operational approaches. FedEx’s express shipping tiers are structured around precise delivery windows, with services like FedEx Priority Overnight guaranteeing delivery by 10:30 AM the next business day in most U.S. locations. Their integrated air-ground network allows for seamless transitions between transportation modes, minimizing handoffs and reducing delivery times.
DHL’s express services are similarly tiered but with a stronger emphasis on international capabilities. Their DHL Express 9:00 and 12:00 services guarantee delivery by specific morning hours, catering to time-critical business needs. DHL’s extensive customs clearance expertise—a result of their international focus—often translates to faster border crossings and reduced delays for international shipments.
Both carriers have developed specialized e-commerce solutions that integrate warehousing with last-mile delivery. FedEx Fulfillment combines inventory management, order processing, and shipping in a single service, while DHL eCommerce offers similar end-to-end solutions with particular strength in cross-border e-commerce. The integration of these services eliminates handoffs between providers, significantly reducing overall delivery timeframes for online retailers.
Strengths and Weaknesses
FedEx Strengths
- Extensive air fleet (650+ aircraft) enabling rapid long-distance delivery
- Superior domestic U.S. network with comprehensive coverage
- Advanced package tracking technology with minute-by-minute updates
- Strong overnight and same-day delivery capabilities
- Integrated multimodal transportation network reducing handoffs
FedEx Limitations
- Higher average costs for international shipping
- Less extensive global network compared to DHL
- More complex customs processes for some international destinations
- Limited presence in certain developing markets
- Less flexible delivery options in some international regions
DHL Strengths
- Unmatched global network spanning 220+ countries and territories
- Superior customs clearance expertise reducing border delays
- Specialized knowledge of emerging markets and challenging regions
- Strong European and Asia-Pacific infrastructure
- Comprehensive international express services with time-definite options
DHL Limitations
- Less developed U.S. domestic network
- Smaller air fleet than FedEx (260+ aircraft)
- Limited same-day options in certain markets
- Higher costs for U.S. domestic shipping
- Less integrated ground transportation in North America
FedEx’s primary strength lies in its massive air fleet—the largest cargo airline in the world—which enables exceptional speed for long-distance shipments. Their Memphis superhub processes over 1.5 million packages nightly with a 99.8% sorting accuracy, minimizing delays caused by misrouting. However, this infrastructure advantage is most pronounced within North America; FedEx’s international capabilities, while strong, don’t match their domestic dominance.
DHL excels in international logistics, particularly in customs clearance efficiency. Their specialized teams navigate complex import/export regulations across diverse markets, often reducing clearance times by 30-40% compared to competitors. This expertise is especially valuable for shipments to regions with challenging regulatory environments like South America and Africa. However, DHL’s relatively limited U.S. domestic infrastructure means they can’t match FedEx’s speed for intra-U.S. deliveries.
Speed and Delivery Accuracy
When examining delivery speed, the data reveals distinct patterns based on geography and service type. For U.S. domestic shipments, FedEx consistently outperforms DHL with average delivery times of 1.9 days for FedEx Express compared to 2.3 days for DHL Express. This advantage extends to on-time delivery rates, where FedEx achieves 91.3% on-time performance for domestic express shipments versus DHL’s 87.6%, according to 2023 Xeneta logistics performance data.
The situation reverses for international shipments, particularly those crossing multiple regions. DHL Express Worldwide delivers in an average of 2.8 days for intercontinental shipments, compared to FedEx International Priority’s 3.2 days. This advantage is most pronounced for shipments between Europe and Asia, where DHL’s average delivery time is 2.5 days versus FedEx’s 3.1 days. DHL’s superior customs clearance capabilities contribute significantly to this speed advantage, with packages spending an average of 35% less time in customs processing.
Both carriers face challenges during peak seasons, but with different impact patterns. FedEx’s on-time delivery rate drops approximately 4.2 percentage points during the November-December holiday season, while DHL experiences a 3.8 percentage point decline. However, DHL maintains better consistency for international shipments during these periods, with only a 2.9 percentage point decline in on-time performance compared to FedEx’s 5.1 percentage point drop. This suggests DHL’s international network may be more resilient to seasonal volume surges.
Innovation and Technology Integration

Both FedEx and DHL have made substantial investments in technology to enhance shipping speed, though with different areas of focus. FedEx’s SenseAware platform provides real-time tracking with environmental monitoring capabilities, allowing for proactive intervention when shipments face potential delays. Their AI-powered dynamic route optimization system, implemented in 2022, has reduced delivery times by an average of 17 minutes per route by continuously recalculating optimal paths based on traffic and weather conditions.
DHL has pioneered predictive analytics through their Resilience360 platform, which anticipates supply chain disruptions before they occur. This system analyzes over 8 million data points daily to identify potential delays and automatically reroute shipments. Their MySupplyChain platform integrates end-to-end visibility across all transportation modes, reducing average transit times by 6.4% through improved coordination between shipping segments.
Both carriers are actively developing autonomous delivery solutions. FedEx’s Roxo delivery robot has completed over 5,000 test deliveries in urban environments, while DHL has deployed over 2,000 warehouse robots globally, increasing sorting speeds by up to 30%. DHL’s Parcelcopter drone delivery system has successfully operated in challenging environments like the mountainous regions of Bavaria and the North Sea island of Juist, demonstrating the potential for dramatically reduced delivery times in remote areas.
“The difference between FedEx and DHL isn’t just about who has more technology, but rather how they’re applying it to solve specific shipping challenges. FedEx excels at optimizing their dense domestic network through AI, while DHL leverages predictive analytics to navigate the complexities of international shipping.”
Sustainability and Environmental Goals

Sustainability initiatives increasingly influence shipping operations, with both carriers making significant commitments that affect their service networks. FedEx has pledged carbon-neutral operations by 2040, investing over $2 billion in vehicle electrification, sustainable energy, and carbon sequestration. Their electric vehicle fleet currently includes more than 3,000 delivery vehicles, with plans to convert their entire pickup and delivery fleet to zero-emission vehicles by 2040.
DHL has set a slightly longer timeline with their commitment to zero emissions by 2050, but with more aggressive interim targets. They currently operate over 27,000 electric delivery vehicles globally (approximately 29% of their fleet), significantly more than FedEx’s electric fleet. DHL’s GoGreen Plus service allows customers to opt for carbon-neutral shipping, with over 80% of their facilities now powered by renewable electricity.
These sustainability initiatives are increasingly affecting routing decisions and delivery speeds. DHL’s optimization algorithms now factor carbon emissions alongside speed and cost, sometimes selecting slightly longer routes that produce significantly lower emissions. Similarly, FedEx’s route density planning has increased the number of packages delivered per mile by 8.6% since 2020, reducing both environmental impact and average delivery times in urban areas through more efficient routing.
Financial Performance and Growth Strategy
Financial performance provides insight into each carrier’s ability to invest in speed-enhancing capabilities. FedEx reported annual revenue of $90.2 billion in fiscal year 2023, with their Express segment accounting for $45.1 billion. Their capital expenditure of $6.2 billion included $2.4 billion specifically allocated to network speed improvements, including automated sorting technology and route optimization systems.
DHL Group (Deutsche Post DHL) generated €94.4 billion ($103.8 billion) in revenue for 2023, with DHL Express contributing €27.6 billion ($30.4 billion). Their strategic investment program allocated €3.9 billion ($4.3 billion) toward automation and digitalization initiatives designed to improve delivery speed and reliability. This included €1.2 billion for their “Strategy 2025” program focused on network optimization and express delivery enhancements.
Regional revenue distribution reveals each carrier’s strategic priorities. FedEx derives approximately 73% of its revenue from North America, reflecting its domestic focus. DHL, conversely, generates only 15% of revenue from the Americas, with 45% coming from Europe and 28% from Asia-Pacific. These allocation patterns directly influence where each carrier concentrates its speed-enhancing investments, with FedEx prioritizing U.S. domestic capabilities and DHL focusing on international and emerging market infrastructure.
Customer Experience and Brand Perception
How do FedEx and DHL compare in customer satisfaction ratings?
According to J.D. Power’s 2023 U.S. Parcel Shipping Satisfaction Study, FedEx scored 806 out of 1,000 points for business customers, while DHL received 791 points. For international shipping, DHL scored higher with 842 points compared to FedEx’s 825. Customer reviews consistently cite FedEx’s domestic tracking accuracy and DHL’s international delivery speed as key satisfaction factors.
Which carrier offers better digital tracking capabilities?
FedEx’s tracking system provides more frequent status updates, with an average of 14 scan points per domestic package compared to DHL’s 9 scan points. However, DHL’s international tracking offers more detailed customs status information and more accurate estimated delivery times, with an average variance of ±2.8 hours versus FedEx’s ±4.1 hours for international shipments.
How do their customer service response times compare?
FedEx’s average customer service response time is 4.2 minutes for phone inquiries and 3.7 hours for email. DHL averages 5.8 minutes for phone support but responds to emails faster at 2.9 hours. DHL’s international help desk receives higher satisfaction ratings (4.2/5) than FedEx’s international support (3.8/5), particularly for complex cross-border shipping issues.
Customer experience significantly influences perceptions of shipping speed, as the perceived delivery time often matters as much as the actual transit duration. FedEx’s tracking interface receives higher usability ratings (4.3/5 versus DHL’s 3.9/5 in G2 crowdsourced reviews), with users particularly valuing the precision of their delivery window estimates. However, DHL’s proactive notification system, which alerts customers to potential delays before they occur, receives higher satisfaction scores (4.5/5 versus FedEx’s 3.7/5).
Brand perception surveys reveal interesting regional variations. In North America, FedEx is generally perceived as the faster carrier (cited by 58% of business customers), while in Europe and Asia, DHL holds this distinction (cited by 62% and 71% of customers, respectively). These perceptions largely align with actual performance data, suggesting that customer experiences accurately reflect each carrier’s regional strengths.
Challenges and Future Outlook

Both carriers face significant challenges that impact their ability to maintain and improve shipping speeds. Labor shortages represent a critical issue, with FedEx reporting a 12% driver vacancy rate in 2023 and DHL facing similar staffing challenges with a 9% vacancy rate across their global operations. These shortages have increased average delivery times by approximately 8-14 hours during peak periods. Both companies are responding with increased automation, with FedEx planning to automate 30% of package sorting by 2026 and DHL targeting 40% by 2025.
Geopolitical disruptions increasingly affect international shipping speeds. The Red Sea crisis beginning in late 2023 forced both carriers to reroute shipments around Africa, adding 7-10 days to transit times between Asia and Europe. DHL’s more extensive ground transportation network in Eurasia provided some advantage, allowing them to shift approximately 18% of affected volume to rail and road alternatives, compared to FedEx’s 7% modal shift capability.
Looking forward, both carriers are investing heavily in predictive logistics. FedEx’s “FedEx Surround” platform, developed in partnership with Microsoft, uses IoT sensors and AI to predict delivery disruptions up to 48 hours in advance. DHL’s “Delivered Within” initiative aims to provide guaranteed delivery within specific hourly windows rather than full-day ranges, supported by their machine learning-based Dynamic Routing Analysis tool. These innovations suggest that competition in shipping speed will increasingly focus on predictability and precision rather than just raw transit time.
“The future of express shipping isn’t just about getting packages from A to B faster—it’s about creating intelligent networks that can guarantee specific delivery windows with near-perfect reliability, even as global conditions become more volatile.”
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Carrier for Your Speed Requirements
Our comprehensive analysis reveals that neither FedEx nor DHL universally outperforms the other in terms of shipping speed. Rather, each carrier excels in specific scenarios based on geography, shipment type, and service level. For U.S. domestic shipments, FedEx consistently delivers faster service with more precise delivery windows and superior tracking visibility. Their extensive domestic infrastructure and larger air fleet give them a clear advantage for time-sensitive shipments within North America.
For international shipping, particularly between Europe, Asia, and emerging markets, DHL generally offers faster transit times and more reliable customs clearance. Their specialized international expertise and more extensive global ground network provide tangible speed advantages for cross-border shipments, especially to challenging destinations. DHL’s international express services consistently outperform in terms of both average delivery time and on-time reliability for intercontinental routes.
When selecting between these carriers, businesses should consider not only raw transit times but also reliability, tracking capabilities, and service consistency during peak periods. For mission-critical domestic U.S. shipments, FedEx remains the speed leader. For complex international logistics, particularly involving multiple regions or developing markets, DHL’s specialized expertise typically translates to faster overall delivery. By matching your specific shipping requirements to each carrier’s demonstrated strengths, you can optimize for both speed and reliability in your logistics operations.