The battle for smartphone market dominance between Apple and Samsung has shaped the mobile industry for over a decade. As these tech giants continue to innovate and compete for global market share, their strategies, strengths, and challenges evolve in response to changing consumer preferences and emerging technologies. This comprehensive analysis examines the current state of their rivalry and explores which company truly leads the global smartphone market in 2024.
Company Overview
Apple’s headquarters in Cupertino (left) and Samsung’s headquarters in Seoul (right) reflect their distinct corporate identities
Founded in 1976, Apple revolutionized the smartphone industry with the iPhone’s introduction in 2007. The company maintains exclusive control over both hardware and software through its iOS ecosystem. Apple’s focused product strategy emphasizes premium devices with seamless integration across its service offerings.
Samsung Electronics, a division of the larger Samsung Group founded in 1938, entered the mobile phone market in 1988. The company embraced Android in 2009 and has since developed a diverse portfolio spanning multiple price segments. Unlike Apple, Samsung manufactures many of its own components, including displays, memory chips, and processors.
Core Business and Product Strategy
Apple’s Approach
Apple pursues a premium ecosystem strategy centered on vertical integration. The company offers a limited number of iPhone models at higher price points, focusing on user experience and ecosystem lock-in through services like iCloud, Apple Music, and the App Store. This integration creates significant switching costs for users invested in the Apple ecosystem.
The iPhone generates approximately 52% of Apple’s total revenue, with services growing to represent about 22%. This strategy has positioned Apple as the most profitable smartphone manufacturer globally, despite selling fewer units than some competitors.
Samsung’s Approach
Samsung employs a broad portfolio strategy with devices across all price segments. The company’s flagship Galaxy S and innovative Fold series target premium consumers, while its extensive A-series serves mid-range and budget markets. This approach maximizes market coverage but results in lower average profit margins compared to Apple.
As both a component supplier and device manufacturer, Samsung leverages vertical integration differently than Apple. The company often introduces hardware innovations first (like foldable displays) while relying on Google’s Android for its operating system.

Apple’s focused iPhone lineup (left) contrasts with Samsung’s diverse Galaxy portfolio (right)
Strengths and Weaknesses
Apple’s Strengths
- Unified ecosystem with seamless integration
- Industry-leading chip performance (A-series)
- Strong brand loyalty and premium positioning
- Consistent software updates for 5+ years
- Higher profit margins (42% vs Samsung’s 15%)
- Privacy-focused marketing advantage
Apple’s Weaknesses
- Limited product range and customization
- Higher entry price points (starting at $799)
- Closed ecosystem with restricted interoperability
- Slower adoption of certain hardware innovations
- Declining market share in emerging markets
- Dependency on China for manufacturing
Samsung’s Strengths
- Diverse product portfolio across price segments
- Hardware innovation leadership (displays, cameras)
- Component manufacturing expertise
- Strong presence in emerging markets
- Greater hardware customization options
- Early adoption of new technologies (foldables)
Samsung’s Weaknesses
- Lower profit margins than Apple
- Fragmented software experience
- Shorter software support lifecycle
- Brand perception challenges in premium segment
- Competition from other Android manufacturers
- Less developed services ecosystem
iOS (left) emphasizes simplicity while Android (right) offers greater customization
Innovation and Technology Leadership
Apple’s Innovation Focus
- Silicon Excellence: Apple’s A-series and M-series chips consistently outperform competitors in both performance and efficiency benchmarks
- Computational Photography: Advanced image processing that enhances photo quality beyond hardware capabilities
- Ecosystem Integration: Seamless connectivity across devices (Continuity, Handoff, Universal Clipboard)
- Privacy Features: App Tracking Transparency, Private Relay, and on-device processing
- Software Optimization: Tight hardware-software integration enabling better performance with less RAM
Samsung’s Innovation Focus
- Display Technology: Pioneer in flexible OLED, higher refresh rates, and brightness capabilities
- Form Factor Innovation: Leading the foldable category with Z Fold and Z Flip series
- Camera Hardware: Early adoption of high-megapixel sensors, periscope zoom, and multiple lens arrays
- Memory Technology: Advanced RAM and storage solutions
- Charging Capabilities: Faster wired and wireless charging standards
The innovation approaches of these companies reflect their broader business strategies. Apple focuses on refinement, user experience, and ecosystem value, often waiting to implement new technologies until they can be seamlessly integrated. Samsung emphasizes hardware advancement and being first-to-market with new features, even if the implementation may initially be less polished.
Apple’s custom silicon (left) versus Samsung’s Exynos processor (right) represent different innovation approaches
Sustainability and ESG Commitments
Apple’s Environmental Initiatives
Apple has committed to complete carbon neutrality across its entire business, manufacturing supply chain, and product life cycle by 2030. The company now operates with 100% renewable energy for its corporate operations and has removed plastic from much of its packaging. Apple’s recycling programs, including the innovative Daisy robot for iPhone disassembly, recover valuable materials from old devices.
Recent iPhones incorporate recycled materials including gold, tungsten, and rare earth elements. The company has also improved repairability through its Self Service Repair program, though critics argue these efforts remain insufficient compared to truly repairable designs.
Samsung’s Environmental Initiatives
Samsung has pledged to achieve net zero carbon emissions by 2050 and incorporate recycled materials in all mobile products by 2025. The company’s Galaxy Upcycling program repurposes older smartphones for alternative uses like IoT devices or medical diagnostic tools, extending their useful life.
Samsung has increased its use of recycled plastics and improved energy efficiency across its manufacturing processes. The company has also expanded its take-back programs globally, though its longer-term sustainability roadmap generally lags behind Apple’s more aggressive timeline commitments.

Apple’s Daisy recycling robot (left) and Samsung’s Galaxy Upcycling program (right) address electronic waste
Financial Performance
| Financial Metric | Apple | Samsung |
| Smartphone Revenue (2023) | $200 billion | $85 billion |
| Profit Margin | 42% | 15% |
| Average Selling Price | $950 | $450 |
| R&D Spending (2023) | $29.9 billion | $20.6 billion |
| Revenue Growth YoY | 6.2% | 3.8% |
The financial performance of these companies reveals their fundamentally different business models. Apple captures approximately 80% of the global smartphone industry’s profits while shipping only about 20% of the units. This remarkable profit concentration stems from Apple’s premium pricing strategy, vertical integration, and ecosystem services revenue.
Samsung’s mobile division generates significant revenue but with substantially lower margins. The company’s component businesses (particularly memory and displays) often contribute more to its overall profitability than its smartphone division. This diversified revenue stream provides Samsung with stability but dilutes its focus on maximizing smartphone profitability.
Financial comparison shows Apple’s superior profit margins despite Samsung’s substantial revenue
Brand Image and Customer Loyalty
Apple’s Brand Positioning
Apple has cultivated a premium brand image associated with simplicity, design excellence, and status. The company maintains an industry-leading customer retention rate of 92%, indicating exceptional brand loyalty. This loyalty stems from the ecosystem lock-in effect, consistent user experience, and strong emotional connection to the brand.
Apple’s marketing emphasizes lifestyle integration, privacy, and creativity rather than technical specifications. This approach resonates particularly with consumers in higher income brackets and creative professionals, creating a distinct brand identity that transcends product features.
Samsung’s Brand Positioning
Samsung positions itself as an innovation leader with cutting-edge technology and greater consumer choice. The company’s retention rate of approximately 74% reflects strong but less intense brand loyalty compared to Apple. Samsung’s marketing frequently highlights technical specifications and feature comparisons, directly challenging Apple in advertisements.
The Samsung brand spans numerous product categories beyond smartphones, creating both opportunities for cross-category sales and challenges in maintaining a focused brand message. The company’s broader market coverage attracts a more diverse customer base across various price segments.

Apple’s minimalist retail approach (left) contrasts with Samsung’s technology showcase stores (right)
Global Operations and Supply Chain
Apple relies heavily on contract manufacturers, particularly Foxconn, with approximately 90% of its production concentrated in China. The company has begun diversifying manufacturing to India and Vietnam in response to geopolitical tensions and tariff concerns. Apple’s supply chain management is renowned for its efficiency but has faced challenges related to labor practices, concentration risk, and pandemic disruptions.
Samsung maintains greater manufacturing control with significant in-house production capabilities. The company operates major smartphone manufacturing facilities in Vietnam, India, and South Korea, with less dependency on China than Apple. This diversified manufacturing footprint provided Samsung with greater supply chain resilience during recent global disruptions.
Global manufacturing footprint comparison shows Samsung’s more diversified production network
Challenges and Future Direction
Apple’s Challenges
- Slowing innovation cycle and “peak smartphone” market saturation
- Increasing regulatory scrutiny over App Store practices
- Supply chain concentration risks in China
- Growing competition in services revenue streams
- Pressure to maintain premium pricing amid economic uncertainty
- Balancing privacy focus with AI advancement needs
Samsung’s Challenges
- Intense competition from Chinese manufacturers in mid-range segment
- Difficulty differentiating within the Android ecosystem
- Lower software update commitment compared to competitors
- Balancing portfolio breadth with focused innovation
- Semiconductor business cyclicality affecting overall stability
- Establishing stronger services revenue streams
Future Market Directions
Both companies are investing heavily in artificial intelligence as the next frontier of smartphone differentiation. Samsung has launched Galaxy AI features focusing on communication tools and creative applications, while Apple is expected to unveil its comprehensive AI strategy with iOS 18. The integration of on-device AI capabilities will likely become a key competitive battleground.
Extended reality (XR) represents another emerging frontier, with Apple’s Vision Pro establishing an early premium position in spatial computing. Samsung, in partnership with Google and Qualcomm, is developing its own XR platform to compete in this nascent market. The relationship between smartphones and these new computing platforms will significantly influence future competitive dynamics.

AI features and extended reality integration represent the next competitive frontier
Conclusion: Who Dominates the Smartphone Market?
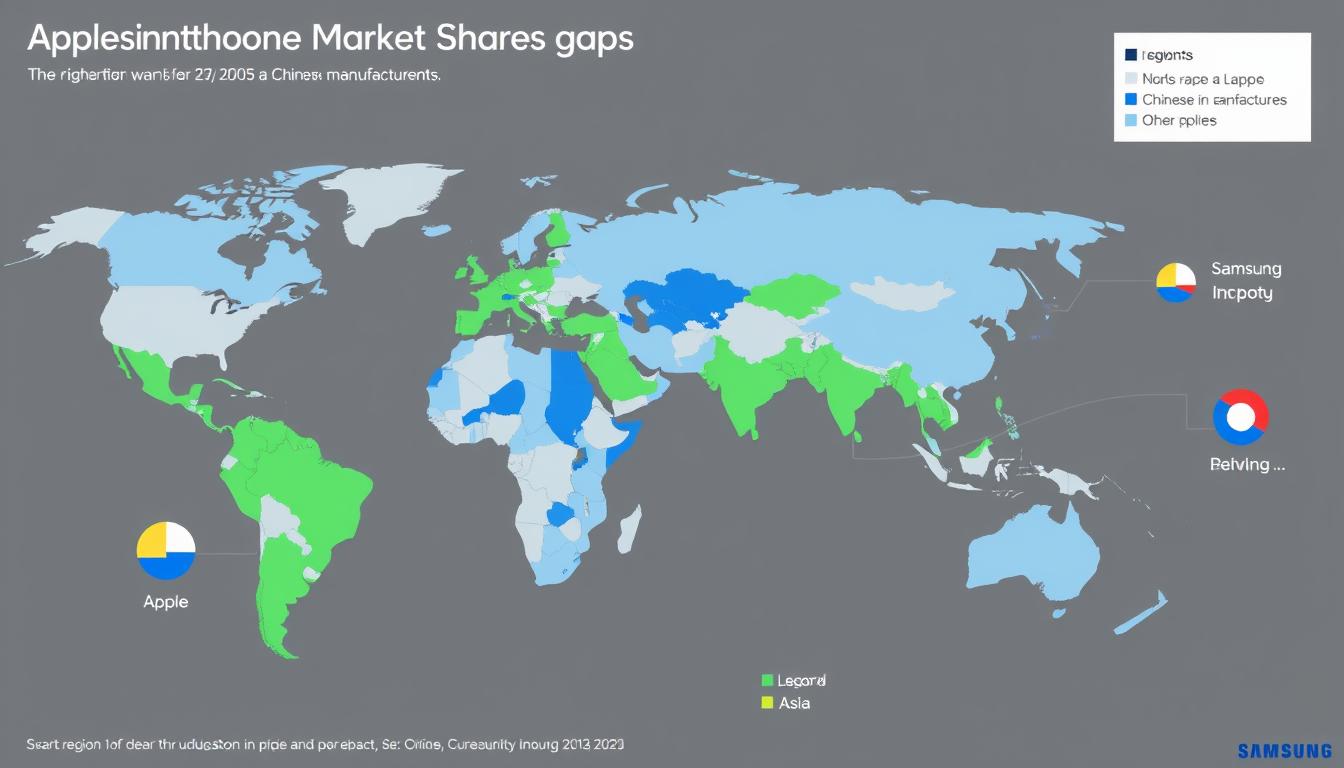
The question of market dominance between Apple and Samsung defies a simple answer. By volume, the companies remain in a virtual tie for global market leadership, with each holding approximately 18-20% of shipments. However, Apple clearly dominates in profitability, capturing around 80% of the industry’s profits while Samsung leads in total units sold across all price segments.
Regionally, Apple dominates North America while Samsung performs better in Europe, with both companies facing growing challenges from Chinese manufacturers in Asia and emerging markets. In the premium segment, Apple maintains a commanding lead, while Samsung offers greater market coverage across all price tiers.
Rather than a single dominant player, the smartphone market in 2024 features two leaders with fundamentally different business models and strengths. Apple excels in premium positioning, ecosystem integration, and profitability, while Samsung leads in hardware innovation, manufacturing capabilities, and market breadth. This competitive dynamic continues to drive innovation that benefits consumers across the entire smartphone industry.

The flagship devices from both companies continue to push smartphone innovation forward