In a world where social media platforms have become the modern town squares, Facebook and Twitter stand as two of the most influential digital arenas shaping public discourse, political movements, and cultural trends. From the Arab Spring to #BlackLivesMatter, these platforms have amplified voices and catalyzed real-world change in unprecedented ways. But which platform truly wields more social influence? Is it Facebook’s massive global reach and sophisticated algorithm, or Twitter’s real-time nature and ability to make headlines?
This analysis delves deep into the battle for social influence between these tech giants, examining their evolution, user demographics, engagement metrics, and impact on society. Using the latest data and expert insights, we’ll explore how each platform has carved its unique niche in the digital landscape and how they continue to shape our collective conversation in distinctly different ways.
Company Background and Evolution
To understand the current battle for social influence, we must first examine how these platforms emerged and evolved over time. Their founding stories and strategic pivots reveal much about their approach to capturing and maintaining social influence. The early days of social media were characterized by experimentation and rapid innovation, as platforms sought to establish their identities in a crowded digital landscape.
For instance, while Facebook focused on connecting friends and family, Twitter carved out a niche for real-time updates and public discourse. These distinct approaches not only shaped their user bases but also influenced how they navigated challenges and opportunities in the evolving social media ecosystem. As these platforms grew, they adapted their features and policies to meet user demands and societal expectations, further entrenching their roles in the social fabric.
Facebook: From Dorm Room to Digital Empire
Founded in 2004 by Mark Zuckerberg and his Harvard classmates, Facebook began as “TheFacebook,” a simple platform for college students to connect. Its evolution has been marked by aggressive expansion and strategic acquisitions that have solidified its position as a social media behemoth:
- 2006: Introduced the News Feed, fundamentally changing how users interact with content
- 2012: Acquired Instagram for $1 billion, expanding its visual social media footprint
- 2014: Purchased WhatsApp for $19 billion, securing dominance in messaging
- 2016: Launched Facebook Live, entering the live streaming space
- 2021: Rebranded as Meta, signaling a pivot toward the metaverse
This evolution reflects Facebook’s strategy of continuous reinvention and expansion beyond its original social networking roots. By acquiring potential competitors and diversifying its offerings, Facebook has built an ecosystem that keeps users engaged across multiple platforms, enhancing its overall social influence.
Twitter: The Real-Time Public Square
Twitter, launched in 2006 by Jack Dorsey, Biz Stone, and Evan Williams, began as a simple SMS-based platform for sharing status updates. Its 140-character limit (later expanded to 280) forced brevity and created a unique communication style that has become integral to public discourse:
- 2009: Introduced the retweet feature, amplifying content sharing capabilities
- 2013: Launched Vine (later discontinued), briefly pioneering short-form video
- 2015: Introduced Moments, curating trending stories
- 2019: Banned political advertising, taking a different approach than Facebook
- 2022: Acquired by Elon Musk, beginning a controversial new chapter
Twitter’s evolution has been characterized by its embrace of real-time communication and its position as a platform for breaking news and public conversation. Unlike Facebook’s expansionist approach, Twitter has largely maintained its core identity while refining its features to enhance real-time engagement.
User Demographics and Growth Trends
The battle for social influence is partly a numbers game, with each platform’s reach and user composition playing crucial roles in determining its impact. Understanding the nuances of these user demographics is essential, as it not only reflects the current state of social media but also influences future marketing strategies and content creation. Let’s examine how Facebook and Twitter compare in terms of user base and demographic distribution, highlighting the implications of these differences for brands and advertisers seeking to maximize their engagement and outreach efforts.
Global Reach and Active Users
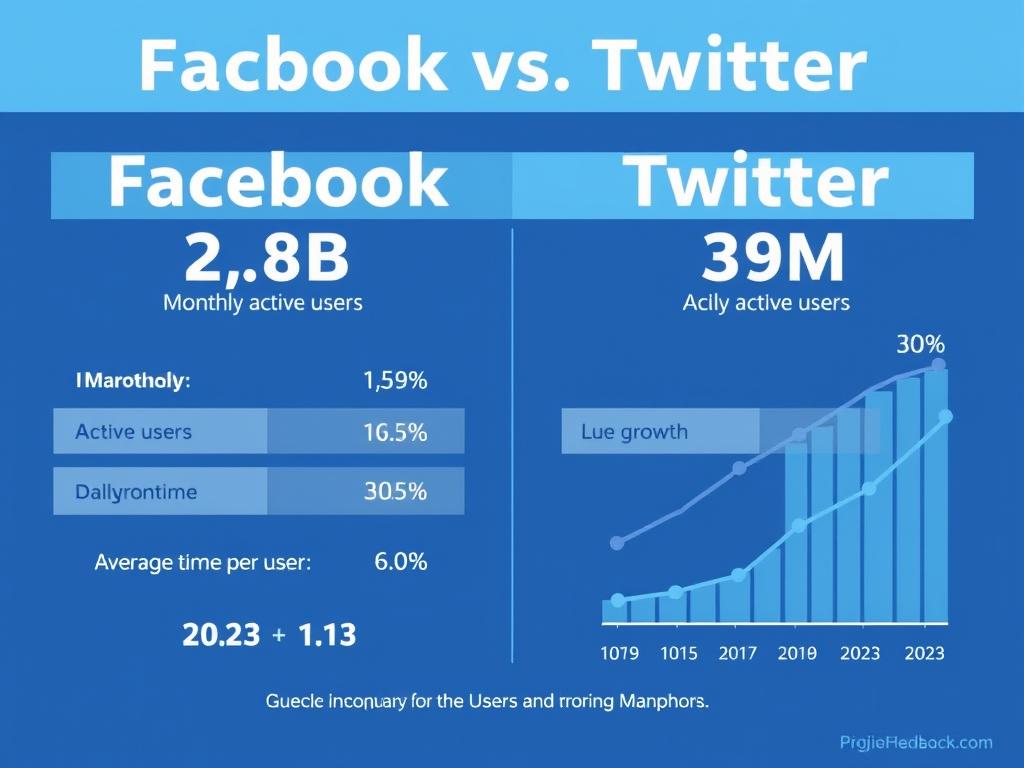
Facebook maintains a commanding lead in terms of sheer user numbers, with approximately 2.9 billion monthly active users as of 2023. This massive reach spans across continents, age groups, and socioeconomic backgrounds, giving Facebook unprecedented global influence.
Twitter, by comparison, reports around 397 million monthly active users. While significantly smaller, Twitter’s user base includes a high concentration of journalists, politicians, celebrities, and thought leaders, amplifying its influence beyond what raw numbers might suggest.
Demographic Distribution
The demographic composition of each platform reveals important distinctions in their spheres of influence:
| Demographic Factor | Influence Implications | ||
| Age Distribution | Broader age range; 25-34 years (31.5%), followed by 18-24 (23.5%) | Younger skew; 18-29 years (42%), followed by 30-49 (27%) | Facebook has greater cross-generational influence; Twitter more influential with younger adults |
| Geographic Reach | Strong global presence; highest user numbers in India, U.S., Indonesia | More concentrated in urban areas; strongest in U.S., Japan, and UK | Facebook has broader global influence; Twitter more influential in developed urban markets |
| Education Level | More evenly distributed across education levels | Higher concentration of college-educated users (42% have college degrees) | Twitter has greater influence among educated professionals and opinion leaders |
| Income Level | More evenly distributed across income brackets | Higher concentration of upper-income users | Twitter has more influence among affluent decision-makers |
| Usage Pattern | Longer, less frequent sessions (avg. 33 minutes daily) | Shorter, more frequent check-ins (avg. 31 minutes daily) | Twitter better for real-time influence; Facebook better for sustained messaging |
Growth Trends and User Engagement
Recent trends in user growth and engagement reveal shifting dynamics in the battle for social influence:
- Facebook: Growth has plateaued in North America and Europe but continues in developing markets. Daily active users increased by just 3% year-over-year in 2022, suggesting market saturation in key regions.
- Twitter: Experienced volatile user growth, with a 16.6% increase in monetizable daily active users in 2021, followed by uncertainty after Elon Musk’s acquisition in 2022.
- Engagement metrics: Facebook users spend more total time on the platform, but Twitter users engage more frequently throughout the day, particularly during breaking news events.
These demographic patterns and growth trends reveal complementary spheres of influence: Facebook’s broad reach gives it extensive influence across diverse populations, while Twitter’s concentration of influential users and real-time nature gives it outsized impact in shaping news cycles and public discourse.
Platform Features and User Engagement
The architectural differences between Facebook and Twitter’s platforms fundamentally shape how users engage with content and, consequently, how social influence manifests on each platform. Facebook’s design fosters a more interconnected and personalized experience, allowing users to interact primarily with content from their close friends and family. This prioritization can lead to a reinforcement of existing beliefs and opinions, as users are often exposed to similar viewpoints within their social circles.
In contrast, Twitter’s structure promotes a more open and fluid exchange of ideas, where trending topics and real-time discussions can reach a broader audience, including those outside of a user’s immediate network. This divergence in platform architecture not only influences the nature of user interactions but also plays a critical role in determining which voices are amplified in public discourse. As a result, the ways in which information spreads and how influence is exerted differ significantly between the two platforms, with Facebook creating echo chambers and Twitter enabling rapid dissemination of diverse perspectives.
Content Algorithms and Feed Structure
Facebook’s Algorithm-Driven Approach: Facebook employs a sophisticated algorithm that prioritizes content based on predicted user interest, relationship strength, and engagement potential. This creates a highly personalized experience that tends to reinforce existing connections and interests.
Key characteristics include:
- Prioritization of content from friends and family over brands and publishers
- Emphasis on content that generates meaningful interactions
- Preference for native content that keeps users on the platform
- Reduced organic reach for business pages, favoring paid promotion
Twitter’s Chronological and Interest-Based Options: Twitter offers both chronological and algorithmic timeline options, with a greater emphasis on recency and trending topics. This creates a more dynamic, real-time experience focused on current events and conversations.
Key characteristics include:
- Option for reverse-chronological feed showing latest tweets first
- “For You” algorithmic feed highlighting relevant content
- Trending topics that surface current conversations
- Greater visibility for content from accounts users don’t follow
These algorithmic differences significantly impact how influence spreads: Facebook’s algorithm tends to create more insular communities where influence builds gradually within networks, fostering a sense of familiarity and trust among users. This gradual accumulation of influence can lead to echo chambers, where ideas are reinforced and dissenting opinions are often sidelined. In contrast, Twitter’s approach facilitates rapid, widespread dissemination of ideas beyond established connections, allowing for a more diverse range of voices to enter the conversation.
This can result in trending topics that capture the attention of users across various demographics, thereby amplifying messages that might otherwise remain unheard. The dynamics of influence on these platforms reflect their underlying structures, with Facebook nurturing close-knit interactions and Twitter promoting a broader, more immediate exchange of ideas that can shape public opinion in real-time.
Engagement Mechanisms and Metrics
Each platform offers distinct mechanisms for engagement that shape how users interact with content and how influence is measured:
| Engagement Feature | Influence Impact | ||
| Primary Engagement Actions | Reactions (Like, Love, Care, etc.), Comments, Shares | Likes, Retweets, Replies, Quote Tweets | Facebook’s nuanced reactions allow for more emotional expression; Twitter’s retweet mechanism enables faster content spread |
| Content Amplification | Shares within networks; Group sharing | Retweets and Quote Tweets; potential for viral spread beyond followers | Twitter enables more rapid, widespread amplification across network boundaries |
| Content Longevity | Longer content lifespan (24-48 hours in feed) | Shorter content lifespan (15-20 minutes for typical tweet) | Facebook allows for sustained influence; Twitter requires timing and frequency |
| Community Features | Groups, Events, Pages | Communities, Lists, Spaces | Facebook’s robust community tools enable deeper, sustained influence within interest groups |
| Content Format Limitations | Virtually unlimited text; multiple media formats | 280 character limit; limited media attachments | Twitter’s constraints force concision and clarity, often increasing message impact |
User Behavior Patterns
The way users interact with each platform reveals important distinctions in how social influence manifests:
- Facebook usage patterns: Typically involves longer, less frequent sessions focused on personal connections, life updates, and group interactions. Users often engage with content from their established networks, creating stronger but more insular influence spheres.
- Twitter usage patterns: Characterized by shorter, more frequent check-ins throughout the day, often driven by breaking news or trending topics. Users regularly engage with content from outside their immediate network, facilitating broader but potentially shallower influence.
According to a 2023 Pew Research study, 54% of Twitter users report getting news from the platform, compared to 44% of Facebook users, highlighting Twitter’s stronger position as an information and news dissemination channel despite its smaller user base.
Stay Updated on Social Media Trends
Want to keep up with the latest developments in the battle for social influence? Subscribe to our newsletter for quarterly reports on platform changes, user trends, and influence metrics.
Impact on Public Opinion and Politics
Perhaps nowhere is the battle for social influence more evident than in the realm of politics and public opinion formation. Both platforms have become essential tools for political communication, but they shape discourse in markedly different ways. Facebook, with its vast user base, allows for targeted messaging that can reach specific demographics, thereby influencing voter behavior through tailored advertisements and curated content.
On the other hand, Twitter’s immediacy and brevity facilitate rapid exchanges of information, making it a go-to platform for breaking news and real-time reactions from politicians and the public alike. This dichotomy illustrates how each platform not only serves as a conduit for information but also actively shapes the narratives surrounding political events, further entrenching their roles in modern political discourse.
Political Communication and Campaigning
Facebook as a Targeted Campaign Tool: Facebook’s sophisticated targeting capabilities have made it the preferred platform for political campaigns seeking to reach specific voter segments with tailored messaging. Its ability to micro-target based on demographics, interests, and behaviors has revolutionized political advertising.
During the 2020 U.S. presidential election, campaigns spent over $1.4 billion on Facebook ads, leveraging the platform’s precise targeting to reach swing voters in key states. The Trump campaign alone spent $89.1 million on Facebook ads in 2020, reflecting the platform’s perceived effectiveness in political persuasion.
Twitter as the Political Pulse: Twitter has established itself as the platform where political news breaks and where politicians can directly address the public without media filtration. Its real-time nature makes it particularly effective for rapid response and shaping the political narrative.
The platform’s influence on political discourse is evidenced by its adoption rate among elected officials: 100% of U.S. senators and 99% of House members maintain active Twitter accounts. Political journalists also heavily rely on Twitter, with 83% reporting it as their primary source for breaking news, according to a 2022 Cision survey.
Case Studies in Political Influence
The 2016 U.S. Presidential Election
The 2016 election provided a stark illustration of how each platform can influence political outcomes:
- Facebook’s role: Became a primary vector for misinformation and foreign interference. According to a Senate Intelligence Committee report, Russian-backed entities reached 126 million Americans through Facebook with divisive content designed to influence the election.
- Twitter’s role: Served as Donald Trump’s primary communication channel, allowing him to bypass traditional media and speak directly to supporters and the public. His tweets generated immediate news coverage, effectively setting the media agenda.
A 2018 study by MIT Technology Review found that false news stories on Facebook were 70% more likely to be retweeted than true stories, highlighting the platform’s vulnerability to misinformation campaigns.
The Arab Spring and Global Movements
Both platforms played crucial but different roles in facilitating political movements:
- Facebook’s contribution: Provided organizational infrastructure for protesters during the Arab Spring, allowing activists to coordinate events and share information privately. In Egypt, the “We Are All Khaled Said” Facebook page, which garnered over 400,000 followers, became a rallying point for the revolution.
- Twitter’s contribution: Amplified protest messages globally and provided real-time updates from the ground. The hashtag #Jan25 during the Egyptian revolution generated over 1.4 million tweets, creating international awareness and pressure.
Content Moderation and Political Speech
The platforms’ approaches to moderating political content reveal fundamental differences in how they conceptualize their influence responsibilities:
Facebook’s Approach: Has generally taken a more hands-off approach to political speech, exempting politicians from fact-checking programs and allowing more controversial content in the name of free expression. This changed somewhat after the January 6, 2021 Capitol riot, when Facebook suspended then-President Trump’s account.
Facebook established an independent Oversight Board in 2020 to review content moderation decisions, creating a quasi-judicial body to handle controversial cases and establish precedents.
Twitter’s Approach: Has been more willing to label or remove political content that violates its policies. In 2020, Twitter began labeling misleading tweets from political figures, including then-President Trump, and eventually permanently suspended his account following the Capitol riot.
Under Elon Musk’s ownership, Twitter has shifted toward a more permissive approach to content moderation, reinstating previously banned accounts and emphasizing “free speech” principles.
These differing approaches to content moderation reflect each platform’s understanding of its role in the information ecosystem: Facebook positions itself as a neutral platform facilitating connections, while Twitter has more explicitly acknowledged its role in public discourse and the responsibilities that entails—though this position has evolved under new ownership.
Advertising Strategies and Revenue Models
The battle for social influence is inextricably linked to the battle for advertising dollars. Each platform’s advertising capabilities and revenue models reveal much about how they leverage their influence. In today’s digital landscape, social media platforms are not just communication tools; they are powerful marketing channels that dictate trends and shape public opinion.
As brands seek to connect with consumers, they must navigate these platforms’ unique advertising ecosystems, which are designed to maximize engagement and conversion. Understanding the intricacies of these systems is crucial for advertisers aiming to effectively reach their target audiences and capitalize on the vast potential of social media.
Advertising Capabilities and Targeting
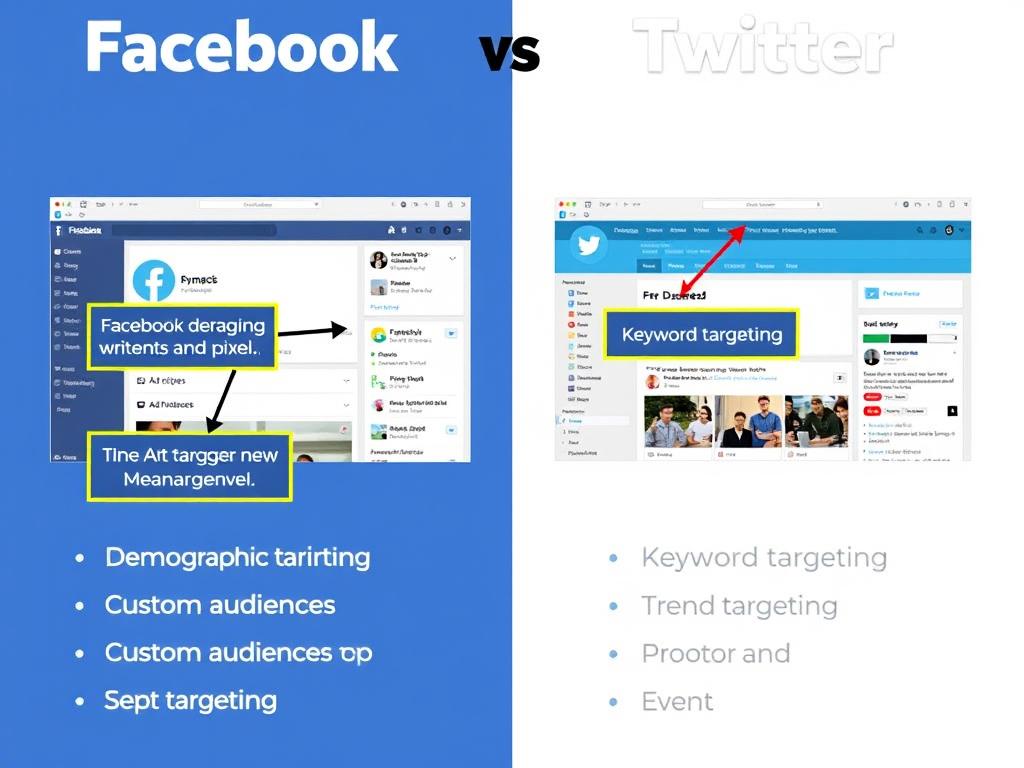
Facebook’s Precision Targeting: Facebook’s advertising platform is renowned for its granular targeting capabilities, allowing advertisers to reach highly specific audience segments based on demographics, interests, behaviors, and connections.
Key strengths include:
- Detailed demographic targeting including age, location, education, and income
- Interest-based targeting drawn from user activity across Meta’s platforms
- Custom and lookalike audiences based on existing customer data
- Retargeting capabilities through the Facebook Pixel
Twitter’s Contextual Relevance: Twitter’s advertising platform emphasizes contextual relevance and real-time engagement, allowing brands to insert themselves into trending conversations and reach users based on their interests and behaviors.
Key strengths include:
- Keyword targeting to reach users discussing specific topics
- Trend targeting to align with current conversations
- Event targeting for time-sensitive promotions
- Follower targeting to reach users with specific interests
Ad Formats and Effectiveness
The platforms offer distinct advertising formats that shape how brands exert influence:
| Ad Format | Influence Effectiveness | ||
| Feed/Timeline Ads | Image, video, carousel, and collection ads integrated into News Feed | Promoted Tweets appearing in user timelines | Facebook offers more visual variety; Twitter ads blend more naturally with organic content |
| Story/Fleets Ads | Full-screen vertical ads between Stories | Discontinued Fleets feature in 2021 | Facebook maintains advantage in immersive, ephemeral content |
| Video Ads | In-stream, feed, and Stories video ads with various placements | Pre-roll and amplify video ads | Facebook offers more placement options; Twitter videos often have higher engagement rates |
| Conversation-Based Ads | Limited options focused on comments | Conversational ads encouraging user engagement and hashtag use | Twitter’s conversation-focused formats generate more public engagement and amplification |
| Trending/Promoted Content | Boosted posts with limited trending capabilities | Promoted Trends appearing in the Trends list | Twitter’s Promoted Trends offer unique visibility in real-time conversations |
Revenue Performance and Business Models
The financial aspects of each platform reveal their market position and sustainability:
- Facebook’s revenue dominance: Meta (Facebook’s parent company) reported $116.6 billion in revenue for 2022, with advertising accounting for 97.5% of that total. The platform’s average revenue per user (ARPU) was $9.41 globally and $50.23 in North America for Q4 2022.
- Twitter’s financial challenges: Twitter reported approximately $5.1 billion in revenue for 2021 (its last full year as a public company), with advertising accounting for about 89% of that total. Its ARPU was estimated at $12.89 in the U.S.
These financial disparities reflect Facebook’s greater scale and more developed advertising ecosystem, which gives it significant advantages in monetizing its influence. However, Twitter’s higher ARPU in the U.S. suggests its influence among valuable demographics remains strong despite its smaller user base.
Advertiser Perception and ROI
How advertisers view each platform provides insight into their perceived influence value:
Facebook advertiser sentiment: Despite privacy challenges and declining organic reach, Facebook remains essential to most digital marketing strategies due to its scale and targeting capabilities. According to a 2022 eMarketer survey, 63% of U.S. marketers planned to increase Facebook ad spending, citing strong ROI and targeting capabilities.
Average Facebook ad metrics:
- Click-through rate (CTR): 0.90%
- Cost per click (CPC): $0.97
- Conversion rate: 9.21%
Twitter advertiser sentiment: Advertisers value Twitter for brand awareness and engagement during cultural moments but often question its direct response effectiveness. Following Elon Musk’s acquisition, many major advertisers paused spending due to content moderation concerns, highlighting the platform’s vulnerability to brand safety issues.
Average Twitter ad metrics:
- Click-through rate (CTR): 0.86%
- Cost per click (CPC): $0.38
- Conversion rate: 0.9-3.0% (varies widely by industry)
These metrics reveal that while Facebook generally delivers stronger conversion performance, Twitter offers more cost-effective clicks, making it valuable for top-of-funnel influence. The platforms thus occupy different but complementary positions in many advertisers’ influence strategies.
Content Moderation Policies and Challenges
How platforms moderate content directly impacts their social influence by determining what voices are amplified or suppressed in the ongoing Facebook vs Twitter social influence debate. Facebook and Twitter have taken notably different approaches to this challenge, each affecting their relationship with followers and raising questions about power dynamics in digital spaces, especially in a city like New York where ideas and insights are constantly shared using Facebook and Twitter.
Policy Frameworks and Enforcement
Facebook’s Comprehensive Guidelines: Facebook maintains extensive Community Standards covering everything from violence and criminal behavior to objectionable content and integrity issues. The platform employs a combination of AI systems and human reviewers to enforce these policies.
Key aspects of Facebook’s approach include:
- Detailed, publicly available policy documentation
- The independent Oversight Board for appealing content decisions
- Quarterly transparency reports detailing enforcement actions
- Tiered enforcement with escalating consequences for violations
Twitter’s Evolving Approach: Twitter’s rules have historically been more concise, focusing on safety, privacy, and authenticity. Under Elon Musk’s ownership, the platform has shifted toward a more permissive approach while introducing new features like Community Notes (formerly Birdwatch) for crowdsourced fact-checking.
Key aspects of Twitter’s approach include:
- Simplified rules focusing on core principles
- Community Notes allowing users to add context to misleading tweets
- Reduced reliance on permanent suspensions
- Increased emphasis on algorithmic amplification over removal
Misinformation and Disinformation Handling
The platforms’ approaches to false information reveal fundamental differences in how they conceptualize their influence responsibilities:
| Aspect | Facebook’s Approach | Twitter’s Approach | Influence Implications |
| Fact-Checking Partnerships | Extensive third-party fact-checking program with over 80 partners globally | Limited partnerships; greater reliance on user-driven Community Notes | Facebook takes more institutional approach; Twitter emphasizes community governance |
| Labeling vs. Removal | Labels misleading content and reduces distribution; removes most harmful misinformation | Previously labeled misleading content; under Musk, shifted toward adding context rather than labeling | Facebook more actively intervenes in information flow; Twitter increasingly relies on counter-speech |
| Political Content | Generally exempts politicians from fact-checking but may reduce distribution | Previously labeled misleading political content; policy less clear under new ownership | Both platforms struggle with balancing political speech and misinformation concerns |
| COVID-19 Misinformation | Removed over 20 million pieces of COVID misinformation; partnered with health authorities | Initially removed COVID misinformation; later relaxed policies under Musk | Platforms’ different approaches shaped public health information landscape |
Hate Speech and Harmful Content
The platforms’ handling of harmful content reflects their different philosophies about free expression and harm prevention:
- Facebook’s proactive approach: Facebook has invested heavily in AI systems to detect hate speech before it’s reported, claiming to proactively identify 95% of hate speech removed from the platform. However, leaked documents have revealed that the company’s systems are far less effective in non-English languages and non-Western markets.
- Twitter’s reactive evolution: Historically, Twitter was criticized for slow responses to harassment and hate speech. The platform gradually strengthened its policies, introducing features like Safety Mode to automatically block accounts using harmful language. Under Musk, some of these policies have been relaxed in favor of “free speech absolutism.”
According to the European Commission’s 2022 evaluation of the Code of Conduct on Countering Illegal Hate Speech Online, Facebook assessed 77.4% of flagged content within 24 hours, compared to Twitter’s 81.5%. However, Facebook removed 69.1% of content deemed illegal hate speech, while Twitter removed only 45.4%, highlighting their different thresholds for intervention.
Transparency and Accountability
How platforms communicate about their moderation efforts affects public trust and regulatory scrutiny:
Facebook’s transparency initiatives: Facebook publishes detailed Community Standards Enforcement Reports quarterly, providing metrics on prevalence of violating content, proactive detection rates, and appeals. The company also maintains a Transparency Center with information about its policies and enforcement.
The establishment of the Oversight Board in 2020 created an unprecedented independent review mechanism, though critics note its limited case volume and Facebook’s ability to choose whether to apply case precedents broadly.
Twitter’s transparency evolution: Twitter has historically published biannual transparency reports with less granular data than Facebook. Under Musk, the company has emphasized making the recommendation algorithm open-source and exposing previous content moderation decisions, though comprehensive transparency reporting has been less consistent.
The platform’s “Twitter Files” releases, giving selected journalists access to internal documents about past moderation decisions, represented an unconventional approach to transparency focused more on past actions than current policies.
These different approaches to transparency reflect each platform’s positioning in the influence ecosystem: Facebook’s more structured, institutionalized approach aims to demonstrate responsible governance of its massive reach, while Twitter’s more ad hoc approach aligns with its identity as a more freewheeling public forum.
Innovations and Technological Advancements
The battle for social influence in social media is increasingly fought through technological innovation, with each platform, including Facebook and Twitter, developing new features and capabilities to enhance user engagement and expand their influence. By using Facebook and Twitter, users can explore various groups and gain insights into the power dynamics between the platforms. This relationship raises questions about how these platforms can better serve their users through ongoing research and review of their practices.
AI and Algorithm Development
Facebook’s AI Investments: Meta has made massive investments in artificial intelligence, both to power its content recommendation systems and to develop new products and features. The company’s AI research division, FAIR (Facebook AI Research), is one of the world’s leading AI research organizations.
Key AI initiatives include:
- Advanced content understanding for better recommendations and moderation
- Computer vision for image and video analysis
- Natural language processing for translation and content analysis
- AI-powered advertising optimization
Twitter’s Algorithmic Approach: Twitter has taken a more focused approach to AI development, concentrating on improving timeline relevance and addressing platform-specific challenges like conversation health.
Key AI initiatives include:
- The “For You” algorithmic timeline recommendation system
- Conversation ranking to highlight relevant replies
- Automated systems to detect coordinated inauthentic behavior
- Image cropping algorithms (though these faced bias controversies)
Facebook’s more extensive AI capabilities give it advantages in content personalization and ad targeting, enhancing its influence through precision. Twitter’s more focused approach aligns with its real-time nature, prioritizing relevance in fast-moving conversations.
Mobile Innovations and Accessibility
Mobile experiences are crucial to social influence in an increasingly smartphone-dominated world:
- Facebook’s mobile evolution: After initially struggling with the transition to mobile, Facebook rebuilt its apps from the ground up, resulting in faster, more engaging experiences. The company has developed lightweight versions like Facebook Lite for emerging markets with limited connectivity, expanding its global influence.
- Twitter’s mobile-first approach: Twitter was designed with mobile in mind from the beginning, and its concise format naturally suited smartphone usage. The platform has continually refined its mobile experience, introducing features like Spaces (audio conversations) that leverage smartphone capabilities.
Both platforms have achieved near-universal mobile accessibility, with over 98% of Facebook users and 80% of Twitter users accessing the platforms via mobile devices. This mobile dominance has fundamentally shaped how social influence operates, making it more immediate, location-aware, and integrated into daily life.
Emerging Technologies and Future Directions
The platforms are pursuing different technological paths that will shape their future influence:
Facebook’s Metaverse Vision: Meta’s rebranding in 2021 signaled its commitment to building the “metaverse,” an immersive virtual reality environment where users can interact, work, and socialize. The company has invested billions in Reality Labs, its division focused on AR/VR technologies.
This strategic pivot represents a bet that social influence will increasingly operate in immersive digital environments rather than traditional social feeds. While still in early stages, this vision could fundamentally transform how people connect and how influence operates.
Twitter’s Audio and Payments Focus: Under Musk’s leadership, Twitter has focused on developing audio features like Spaces and integrating payment capabilities into the platform. The company has applied for money transmitter licenses in multiple U.S. states, suggesting ambitions to become a financial services platform.
These initiatives point toward a vision of Twitter as a more comprehensive public square where conversations, content creation, and commerce converge. By enabling direct monetization, Twitter could enhance its influence among creators and businesses.
These divergent technological paths reflect fundamentally different visions of the future of social influence: Facebook is betting on immersive, virtual experiences becoming the next frontier of human connection, while Twitter is focusing on enhancing its existing strengths as a public conversation platform while adding new utility.
Influence on Culture and Media
Beyond politics and commerce, Facebook and Twitter have profoundly shaped cultural expression and media consumption, each leaving distinct imprints on how we create, share, and engage with culture.
Meme Culture and Viral Content
Facebook’s Community-Based Virality: Facebook’s group functionality has created fertile ground for niche meme communities and interest-based content sharing. The platform’s algorithm tends to amplify content that generates strong engagement within existing communities, creating “filter bubbles” of shared cultural references.
Facebook meme pages and groups often develop their own distinctive styles and inside jokes, fostering a sense of belonging among members. Major meme pages on Facebook can have millions of followers, giving them significant cultural influence within their communities.
Twitter’s Rapid Viral Spread: Twitter’s open network structure and retweet mechanism enable content to spread rapidly beyond its original context, making it particularly effective for launching memes into mainstream awareness. The platform’s emphasis on brevity and wit rewards clever, concise content that can be quickly understood and shared.
Twitter is often where memes first gain traction before spreading to other platforms. The hashtag system allows trends to coalesce quickly, and the platform’s public nature means viral content can reach massive audiences regardless of follower count.
Celebrity and Influencer Culture
The platforms have shaped how public figures engage with audiences and exert cultural influence:
- Facebook’s influencer ecosystem: Facebook (and especially its subsidiary Instagram) has fostered a highly commercialized influencer economy centered around lifestyle content and aspirational imagery. The platform’s emphasis on polished, visual content has created a class of professional influencers who carefully curate their personal brands.
- Twitter’s direct celebrity access: Twitter has become the platform of choice for celebrities to speak directly to fans and the public without media intermediaries. Its text-based, conversational nature rewards authenticity and personality over production value, creating more direct connections between public figures and audiences.
According to a 2022 survey by Influencer Marketing Hub, 67% of brands use Instagram (owned by Meta) for influencer marketing, compared to just 16% using Twitter. However, Twitter influences often have greater perceived authenticity and thought leadership status, particularly in fields like journalism, politics, and technology.
Media Integration and Consumption
Both platforms have transformed how media is produced, distributed, and consumed, but with different emphases:
| Media Aspect | Facebook’s Approach | Twitter’s Approach | Cultural Impact |
| News Distribution | Integrated news partnerships; News Tab feature; emphasis on keeping users on-platform | Link-sharing culture; Moments feature; emphasis on directing users to original sources | Facebook shaped attention economy; Twitter influenced news cycles and journalistic practices |
| Video Content | Facebook Watch; emphasis on longer-form, episodic content; auto-playing videos in feed | Embedded video; emphasis on short clips and highlights; previously owned Periscope for live streaming | Facebook pushed toward social viewing experiences; Twitter emphasized shareable moments |
| Audio Content | Limited audio features; podcast listening within platform | Twitter Spaces for live audio conversations; stronger podcast community | Twitter more influential in audio conversation space; Facebook less focused on audio |
| Creator Monetization | Revenue sharing; Stars tipping system; subscription groups | Super Follows; Ticketed Spaces; Twitter Blue subscription | Both platforms struggling to compete with dedicated creator platforms like YouTube and Substack |
Language and Communication Styles
Perhaps most profoundly, each platform has influenced how we communicate:
Facebook’s impact on communication: Facebook has normalized sharing personal life updates with broad social circles, blurring the lines between private and public communication. The platform’s reaction system has created new emotional shorthand, with “likes” becoming a form of social currency and validation.
Facebook’s algorithm-driven feed has also encouraged more emotionally provocative content, as posts that generate strong reactions receive greater visibility. This has contributed to more polarized discourse and “engagement bait” tactics.
Twitter’s impact on communication: Twitter’s character limit has fostered a culture of concision and cleverness, rewarding those who can communicate effectively in limited space. The platform popularized conventions like hashtags, which have spread across the internet and even into spoken language.
Twitter’s public, conversational nature has also normalized direct engagement with strangers around shared interests or opinions, creating new forms of ambient community. The platform’s emphasis on real-time commentary has accelerated cultural response cycles.
These linguistic and communicative influences extend far beyond the platforms themselves, shaping how people express themselves across digital spaces and even in offline contexts. The phrases “Facebook official” and “Tweet through it” have entered the cultural lexicon, reflecting each platform’s distinctive impact on communication norms.
Regional Popularity and Market Penetration
The global battle for social influence plays out differently across regions, with each platform holding varying levels of dominance and cultural significance around the world. As users navigate social media, they often search for insights into how to use Facebook and Twitter effectively, reflecting the evolving relationship between these platforms. This dynamic creates opportunities for media review and research, as individuals seek to understand the power of one another’s online presence and the items and services they promote.
Geographic Distribution and Usage Patterns
Facebook’s Global Reach: Facebook maintains strong presence across most global markets, with particularly high penetration in:
- India: 329.7 million users, the largest country user base
- Southeast Asia: 89% of internet users in the Philippines and 84% in Thailand use Facebook
- Latin America: 82% of internet users in Mexico and 78% in Brazil are active on the platform
- Africa: Facebook is often the primary internet experience in countries like Nigeria and Kenya
Twitter’s Strategic Strongholds: Twitter has more concentrated popularity in specific markets:
- United States: 77.75 million users, its largest market
- Japan: 58.95 million users, with exceptionally high engagement
- Middle East: Particularly influential in Saudi Arabia and Turkey
- United Kingdom: 19.05 million users, with strong media and political usage
Cultural and Political Significance by Region
The platforms’ influence varies dramatically by region, shaped by local cultural, political, and technological factors:
| Region | Facebook’s Influence | Twitter’s Influence | Key Factors |
| North America | Declining among younger users; strong among older demographics; politically polarizing | Highly influential in media, politics, and cultural discourse; central to political communication | High smartphone penetration; competitive social media landscape; political polarization |
| Europe | Facing regulatory scrutiny; strong user base but declining engagement; privacy concerns | Significant in political discourse; strong in UK, Spain, and Turkey; less dominant than in US | Strong regulatory environment (GDPR); multiple language markets; privacy-conscious users |
| Asia-Pacific | Dominant in Southeast Asia; banned in China; facing competition in Japan and Korea | Exceptionally strong in Japan; growing in India; banned in China | Mobile-first internet adoption; strong local competitors; varying regulatory approaches |
| Middle East | Widely used but heavily monitored; significant for business and personal connections | Disproportionately influential; central to political discourse in Saudi Arabia, UAE, and Turkey | Young, digitally connected population; government monitoring; political restrictions |
| Latin America | Extremely high penetration; often the primary internet experience; WhatsApp (owned by Meta) dominance | Significant in political discourse, particularly in Brazil, Mexico, and Argentina | Mobile-first connectivity; data cost concerns; strong community orientation |
| Africa | Dominant social platform; Free Basics program controversial but widely used | Limited to urban elites in most countries; influential in Nigeria and South Africa | Limited connectivity; data cost barriers; mobile-first internet adoption |
Localization Strategies and Adaptations
How each platform adapts to local markets reveals their approach to extending influence globally:
Facebook’s Localization Approach: Facebook has invested heavily in making its platform accessible and relevant across diverse markets:
- Language support: Available in 111 languages with advanced translation features
- Connectivity initiatives: Free Basics program providing limited internet access in developing markets
- Lite versions: Facebook Lite app optimized for low-bandwidth environments
- Local content partnerships: Collaborations with regional media and content creators
Twitter’s Localization Approach: Twitter has taken a more targeted approach to localization, focusing on key markets:
- Language support: Available in 34 languages
- Regional trending topics: Localized trending sections highlighting regional conversations
- Market-specific features: Features like Fleets (now discontinued) tested in Brazil before global rollout
- Local content policies: Compliance with country-specific legal requirements
Facebook’s more comprehensive localization efforts have helped it achieve greater global penetration, particularly in developing markets. Twitter’s more focused approach has created deeper engagement in specific markets where its format aligns well with local communication styles and needs.
Regulatory Challenges and Market Access
Government regulations and restrictions significantly impact each platform’s global influence:
- Banned markets: Both Facebook and Twitter are banned in China, with its 1 billion+ internet users. Twitter is also restricted in countries including Iran, North Korea, and Turkmenistan. Facebook has faced temporary bans in countries including Turkey, Pakistan, and Uganda during political tensions.
- Data localization requirements: Countries including Russia, India, and Vietnam have implemented data localization laws requiring platforms to store user data locally, creating compliance challenges.
- Content regulation: The European Union’s Digital Services Act, Germany’s NetzDG law, and similar regulations worldwide increasingly require platforms to remove illegal content quickly or face significant penalties.
These regulatory challenges have forced both platforms to navigate complex global governance landscapes, sometimes making compromises that affect their influence and operations in specific regions. Facebook’s greater resources have generally allowed it to adapt more effectively to varying regulatory requirements, though both platforms face ongoing challenges as digital governance evolves worldwide.
Future Outlook and Strategic Plans
As the battle for social media influence continues to evolve, both Facebook and Twitter are pursuing distinct strategies to maintain and expand their relevance in an increasingly competitive digital landscape. Users often search for ways to use Facebook and use Twitter effectively, and insights into their strategies can provide valuable information for groups and individuals alike. This review of their approaches highlights the personality of each platform and the services they offer, shedding light on their success in this dynamic environment. Questions about how to use these sites effectively can lead to better understanding and more effective engagement.
Meta’s Vision: Beyond Traditional Social Media
Facebook’s parent company Meta is making a bold, expensive bet on the metaverse as the next frontier of digital connection and influence. This strategic pivot represents an attempt to define the future of social interaction before competitors can:
- Metaverse development: Investing billions in building immersive virtual environments where users can interact, work, and socialize
- AR/VR hardware: Continuing to develop Quest VR headsets and AR glasses to provide access points to these new experiences
- AI advancement: Leveraging artificial intelligence to create more personalized, engaging experiences across its platforms
- Creator economy: Building tools and monetization options to attract content creators to its ecosystem
This strategy faces significant challenges, including skepticism about metaverse adoption, regulatory scrutiny, and competition from established gaming and virtual world platforms. Meta’s Q4 2022 earnings revealed that Reality Labs, its metaverse division, lost $13.7 billion in 2022 alone.
Industry analysts are divided on the viability of this approach. Gartner predicts that by 2026, 25% of people will spend at least one hour per day in the metaverse, suggesting potential for Meta’s vision. However, others argue that the company is overinvesting in an unproven concept while its core social platforms face growing challenges.
Twitter’s Reinvention Under Musk
Since Elon Musk’s acquisition in late 2022, Twitter has undergone dramatic changes aimed at transforming the platform’s business model and influence approach:
- Twitter Blue: Expanding the subscription service with features including verification, reduced ads, and longer posts
- Payment infrastructure: Building payment capabilities to enable financial transactions between users
- Content moderation shifts: Moving toward less restrictive content policies while introducing Community Notes for context
- Algorithm transparency: Committing to make recommendation algorithms more transparent and user-controllable
These changes represent a fundamental reimagining of Twitter’s business model, moving away from heavy reliance on advertising toward a more diversified approach incorporating subscriptions, payments, and potentially commerce.
The transition has been turbulent, with significant staff reductions, advertiser exits, and technical challenges. However, Musk’s vision of Twitter as a comprehensive “everything app” similar to China’s WeChat presents an ambitious alternative to Meta’s metaverse focus.
Competitive Threats and Opportunities
Both platforms face evolving competitive landscapes that will shape their future influence:
| Competitive Factor | Impact on Facebook | Impact on Twitter | Future Influence Implications |
| TikTok’s Rise | Major threat to user attention, particularly among younger demographics | Less direct competition due to different content format and use case | Both platforms likely to adopt more short-form video features; Facebook faces greater pressure to retain younger users |
| Messaging Platforms | Owns WhatsApp and Messenger; well-positioned in private communication | Limited presence in messaging; DMs secondary to public conversation | Facebook’s ownership of major messaging platforms provides influence advantages as communication shifts more private |
| Decentralized Social | Potential long-term threat to centralized control model | More immediate challenge; Mastodon gained users during Twitter’s transition | Both may need to adapt to more open, interoperable models to maintain influence |
| AI-Generated Content | Investing heavily in AI; potential to enhance personalization | Could change nature of conversation; challenges for verification | Both platforms will need to balance AI content opportunities with authenticity concerns |
| Regulatory Pressure | Facing antitrust scrutiny and potential forced divestiture of acquisitions | Less antitrust pressure but increasing content regulation globally | Regulatory outcomes could fundamentally reshape both platforms’ reach and business models |
Analyst Predictions and Expert Insights
Industry experts offer varying perspectives on the future of these platforms’ social influence:
“Facebook’s core platform may continue to lose cultural relevance in developed markets, but Meta’s portfolio approach—including Instagram, WhatsApp, and future metaverse products—positions it to maintain significant influence across different demographic segments and use cases. The company’s greatest challenge will be navigating the transition to new platforms without alienating its massive existing user base.”
“Twitter’s influence has always exceeded its user numbers due to its position as the platform of choice for journalists, politicians, and thought leaders. Under Musk, the platform risks losing some of this elite influence if content moderation changes drive away key users. However, if it can successfully diversify its business model while maintaining its core as a real-time information network, it could emerge stronger and more influential in specific domains.”
The consensus among analysts suggests that while both platforms will remain influential, their spheres of influence are likely to become more distinct: Meta focusing on immersive social experiences across multiple platforms, and Twitter potentially becoming a more specialized but still crucial platform for real-time information and public discourse.
As users become more selective about their social media usage and new platforms continue to emerge, the battle for social influence is likely to become more fragmented and context-specific, with different platforms dominating different aspects of digital social experience.
Conclusion: The Ongoing Battle for Social Influence
The comparison between Facebook and Twitter reveals not a simple winner in the battle for social influence, but rather two platforms with distinct and complementary forms of influence in our digital society.
Facebook’s massive scale, detailed targeting capabilities, and comprehensive ecosystem give it unparalleled reach and the ability to shape personal connections and communities across demographics. Its influence is broad and deeply embedded in everyday social interactions, particularly in developing markets where it often serves as a primary internet experience.
Twitter’s influence, while reaching fewer users, is amplified by its position as the platform of choice for journalists, politicians, celebrities, and thought leaders. Its real-time, public nature makes it uniquely powerful in shaping breaking news, public discourse, and cultural moments. A single tweet can make headlines worldwide in a way that Facebook posts rarely do.
As we look to the future, both platforms face significant challenges: Meta must justify its expensive metaverse bet while maintaining engagement across its existing platforms; Twitter must stabilize after a tumultuous transition and prove that its new direction can sustain its influence while building a viable business model.
What’s clear is that the battle for social influence will continue to evolve as user preferences change, new competitors emerge, and regulatory frameworks develop. The most successful platforms will be those that can adapt to these changes while maintaining their core value propositions that keep users engaged and influential voices present.
For users, marketers, and society at large, understanding the distinct forms of influence these platforms wield is crucial for navigating our increasingly digital social landscape. Rather than asking which platform “wins” the battle for social influence, perhaps the more important question is how we can harness the unique strengths of each platform while mitigating their potential harms.