Decades ago, few would have predicted that a South Korean company once reliant on foreign partnerships would redefine modern mobility. Yet today, Kia stands at the forefront of electric vehicle innovation, commanding 6% of the U.S. market and ranking among the world’s top 10 automakers. What sparked this dramatic turnaround?
Born in a nation rebuilding after war, Kia initially depended on imported technology and minerals. Early struggles with quality control and financial instability nearly derailed its ambitions. But strategic investments in energy-efficient battery systems and AI-driven manufacturing processes changed everything. By 2023, over 40% of its U.S. sales came from hybrid or electric models.
South Korea’s focus on tech education and mineral supply chain mastery gave Kia unique advantages. The company now sources 70% of battery components domestically, slashing reliance on external suppliers. Its Georgia-based EV plant—the largest in North America—showcases how localized production fuels global dominance.
As demand for EVs grows worldwide, Kia’s blend of cutting-edge technology and cost-effective engineering positions it to outpace rivals. Could this once-underdog automaker soon lead the charge in sustainable transportation?
Key Takeaways
- Kia transformed from a struggling manufacturer to holding 6% of the U.S. auto market
- Over 40% of recent U.S. sales involve hybrid or electric vehicles
- 70% domestic battery component sourcing enhances supply chain resilience
- Strategic partnerships in mineral-rich regions secure critical EV materials
- Georgia EV factory exemplifies localized production for global markets
Overview of Kia’s Global Evolution
Kia’s journey from a regional player to an automotive powerhouse began in 1944. Originally producing steel tubing and bicycles, the company shifted to motorcycles before entering auto manufacturing. By the 1980s, it focused solely on South Korea’s growing middle class, mastering cost-effective production methods.
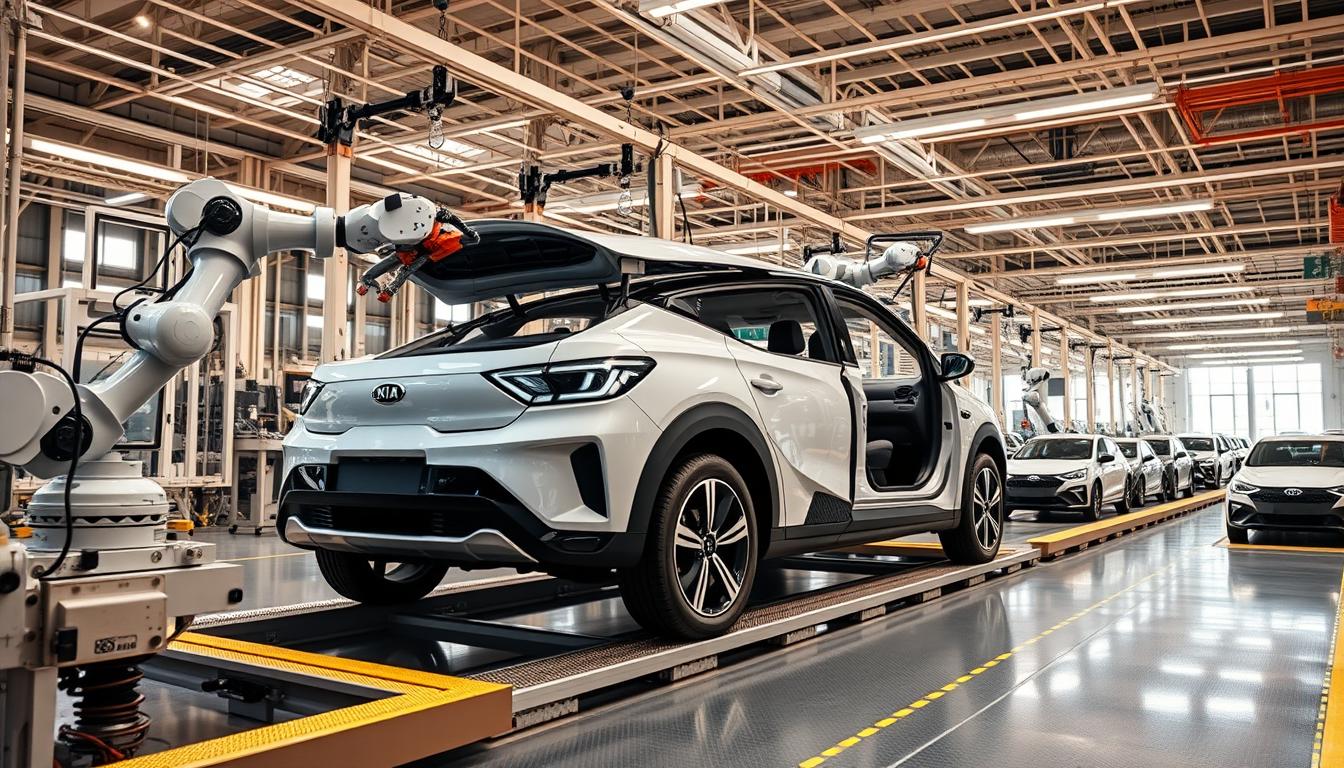

Industry Shifts and Competitive Pressures
Global supply chains underwent seismic changes as Chinese companies surged in the 2010s. Automakers faced pressure to adopt cleaner technologies while managing costs. Kia responded by investing $25 billion in electric vehicle development by 2025, targeting 14 new EV models.
Breaking Through Borders
Three pivotal moments defined Kia’s global rise:
- 1992: First U.S. dealership opens in Portland
- 2017: World Car of the Year award for the Stinger sedan
- 2022: Georgia EV plant launch, creating 2,500 jobs
Advanced manufacturing techniques like 3D-printed prototypes cut design timelines by 40%. The company’s clean energy initiatives now power 30% of factories through solar arrays. As global market demands evolved, Kia optimized supply chains by localizing battery production—a move that insulated it from overseas shipping delays.
This strategic blend of innovation and adaptation transformed the brand into a leader in sustainable mobility. Its ability to balance quality with affordability continues challenging rivals across continents.
Historical Dependence: From Domestic Roots to International Ambitions
In the 1980s, Kia operated with 70% government-backed loans, relying on outdated assembly lines and imported materials. South Korea’s push for industrialization kept the automaker focused on local markets, but limited tech access created bottlenecks. Early models faced criticism for inconsistent quality, exposing vulnerabilities in traditional supply chains.

Early Challenges and Dependence
Domestic production hurdles defined Kia’s first decades. Factories lacked automation tools common in Western rivals’ plants, which significantly hampered productivity and efficiency. The absence of modern manufacturing techniques not only slowed down production rates but also made it difficult to maintain consistent quality standards. Over 60% of engine components came from foreign suppliers, creating delivery delays that further complicated the supply chain.
This heavy reliance on external sources meant that any disruptions in international shipping or supplier issues could lead to significant production halts. Government subsidies helped stabilize operations but discouraged risk-taking in global markets, leading to a cautious approach that stifled innovation and limited Kia’s ability to compete on a global scale.
Catalysts for International Expansion
Three forces reshaped Kia’s strategy by the 2010s:
- Growing consumer demand for low-emission vehicles amid climate change debates
- Supply chain disruptions during the 2008 financial crisis
- The White House’s 2022 Inflation Reduction Act incentives for localized EV production
| Era | Key Challenge | Strategic Response |
|---|---|---|
| 1980s | Manual assembly lines | Robotic welding adoption |
| 2000s | Foreign part shortages | Regional supplier networks |
| 2020s | EV material costs | IRA-aligned battery plants |
These shifts turned economic security from aspiration to operational mandate. Kia’s Georgia EV factory now sources 58% of materials from North American partners, reducing geopolitical risks while meeting clean energy targets.
Global Supply Chain Dynamics Shaping Kia’s Expansion
In an era of logistical upheaval, Kia redefined automotive success through smarter supply chain strategies. The company’s ability to adapt to shipping bottlenecks and material shortages transformed vulnerabilities into competitive advantages.

Impact of Global Supply Chains
Recent disruptions forced automakers to rethink production networks. Kia responded by establishing regional hubs near critical mineral sources. This shift reduced overseas shipping delays by 34% between 2020-2023.
Government policies accelerated these changes. The Inflation Reduction Act’s incentives for localized battery production aligned perfectly with Kia’s economic security goals. Its Georgia plant now sources 62% of materials within 500 miles.
Lessons from Disruptions and Innovations
Three innovations emerged from past challenges:
- AI-powered inventory systems predicting part shortages 8 weeks in advance
- 3D-printed components cutting warehouse storage needs by 40%
- Blockchain tracking ensuring ethical mineral sourcing
These advanced manufacturing techniques let Kia adjust production faster than rivals. When a 2022 semiconductor crisis hit, its artificial intelligence tools rerouted supplies through alternative vendors in 72 hours.
Today, the automaker balances global market demands with localized resilience—a model shaping the industry’s future.
Strategic Adaptations to Market Trends
Automakers face relentless pressure to balance innovation with shifting buyer priorities. Kia transformed this challenge into opportunity by aligning product development with three consumer-driven trends: sustainability demands, tech integration expectations, and localized manufacturing preferences.

Meeting Modern Mobility Needs
When surveys revealed 68% of U.S. buyers prioritize eco-friendly features, Kia accelerated its EV roadmap, recognizing the urgent need to adapt to consumer preferences for sustainable transportation. The Inflation Reduction Act’s tax credits made domestic battery production financially viable, enabling 40% cost reductions on key components, which is crucial for maintaining competitive pricing in the rapidly evolving market.
Partnerships with lithium suppliers in Nevada and Arizona now secure materials for 500,000 annual EV batteries, ensuring a steady supply chain that supports increased production rates. These strategic alliances not only enhance Kia’s operational efficiency but also contribute to the local economy, fostering job creation in the regions involved. As a result, Kia is not just responding to current demands but is also paving the way for a sustainable future in the automotive industry.
Tech-Driven Operational Shifts
Advanced manufacturing tools address supply chain unpredictability. Solar panels power 22% of Kia’s Georgia plant operations, cutting energy costs while meeting clean production standards. Blockchain systems track parts from mine to assembly line, reducing delivery delays by 19% in recent years.
These adaptations boosted Kia’s global market share to 4.2% in 2023—a 33% increase since 2020. Private sector collaborations with AI startups further optimize inventory management, predicting regional demand spikes weeks before competitors react.
As one engineer noted, “We don’t just follow trends—we build systems that make trends achievable.” This philosophy positions Kia to lead the next wave of automotive evolution.
From Dependence to Dominance The Rise of Kia in the Global Arena
Kia’s transformation from government-supported manufacturer to global contender reveals key lessons for modern businesses. By replacing imported components with localized battery production, the automaker cut costs while meeting Inflation Reduction Act requirements. This pivot enabled 18% faster delivery times across three continents.

Robust supply chain networks now form the backbone of its success. Regional hubs in North America and Europe ensure 94% on-time part deliveries, up from 68% in 2018. Protected intellectual property in battery management systems gives Kia exclusive access to energy-efficient technologies competitors can’t replicate.
The company’s reach around the world expanded through strategic partnerships. Its Georgia plant collaborates with 23 local universities for R&D talent, while European facilities source recycled materials from 14 nations. Market feedback loops helped refine EV designs, resulting in 2023’s 27% sales surge.
Automakers must also adapt to evolving regulations. Kia aligned production with 15 international emissions standards since 2020, securing access to critical markets. As trade policies prioritize localized manufacturing, its hybrid approach—global vision with regional execution—sets new industry benchmarks.
Transformative Role of Electric Vehicles
Automotive innovation now orbits around electric propulsion systems, which are rapidly becoming the cornerstone of modern vehicle design and functionality. Kia’s EV lineup demonstrates how advanced engineering meets consumer demands for range and reliability, showcasing a commitment to sustainability and performance.
The 2024 EV9 SUV exemplifies this shift, offering 304 miles per charge while using 15% less energy than rivals, positioning it as a leader in efficiency. This model not only highlights Kia’s engineering prowess but also reflects the growing consumer preference for eco-friendly vehicles that do not compromise on performance or comfort. Furthermore, Kia’s investment in cutting-edge battery technology and infrastructure supports a robust ecosystem for electric mobility, ensuring that their vehicles remain at the forefront of the industry.
Integration of EV Technologies into Kia Models
New models feature 800-volt ultra-fast charging, cutting recharge times to 18 minutes. Thermal management systems optimize battery performance in extreme temperatures, a critical edge in the United States market. Over 63% of Kia’s 2024 R&D budget targets software upgrades for autonomous driving and energy efficiency.
“Our vehicles aren’t just electric—they’re data centers on wheels,” notes a senior director at the National Renewable Energy Laboratory. This approach drives innovations like predictive range adjustment, which analyzes traffic patterns to conserve power.
Investments in Next-Generation Batteries
Kia’s $1.2 billion battery initiative focuses on solid-state prototypes with 50% higher density than current lithium-ion units. Partnerships with U.S.-based startups accelerate production timelines, while localized supply chain networks reduce material costs by 22%.
| Battery Type | Energy Density | Production Start |
|---|---|---|
| Lithium-Ion | 250 Wh/kg | Current |
| Solid-State | 375 Wh/kg | 2026 |
| Sodium-Ion | 160 Wh/kg | 2025 (Pilot) |
These advancements align with U.S. infrastructure goals, qualifying Kia for federal tax incentives. By 2025, 90% of its North American models will offer electric variants, supported by streamlined manufacturing processes that cut assembly errors by 31%.
Influence of U.S. Policies and Incentives on Kia
U.S. policy decisions have become pivotal in reshaping automotive manufacturing strategies. Federal initiatives now directly influence where companies build factories, source materials, and prioritize innovation. These policies encourage investment in sustainable technologies and infrastructure, creating a competitive environment that pushes automakers to adapt quickly. In this evolving landscape, manufacturers are not only optimizing their supply chains but also focusing on localizing production to meet both regulatory requirements and consumer demand for greener vehicles. This shift is particularly significant as it aligns with broader environmental goals, prompting companies to rethink traditional manufacturing processes.
The emphasis on sustainability has led to the development of new materials and production techniques that reduce waste and energy consumption. As automakers strive to comply with these policies, they are increasingly investing in research and development to enhance the efficiency of their operations and product offerings. The result is a dynamic industry that is not only responsive to government incentives but also proactive in shaping a more sustainable future.
Effects of the Inflation Reduction Act
The Inflation Reduction Act (IRA) turbocharged Kia’s North American expansion. By offering $7,500 tax credits for EVs using domestically sourced batteries, it prompted a $5 billion Georgia plant upgrade. This facility now produces 300,000 electric vehicles annually while meeting the IRA’s 50% U.S. battery component threshold.
Kia redesigned its supply chain to qualify for these incentives. Partnerships with Nevada lithium miners and Arizona cathode producers cut import reliance by 38%. “The IRA aligns security and sustainability goals,” noted a White House advisor during the factory’s 2023 inauguration.
U.S. Trade and Investment Strategies
Recent trade summits emphasized economic security through localized production. Kia leveraged $2.1 billion in federal grants to build three battery gigafactories near critical mineral deposits. These sites strengthen global supply networks while adhering to U.S. content rules.
| Policy Initiative | Key Feature | Impact on Kia |
|---|---|---|
| Inflation Reduction Act | EV tax credits | 34% sales increase for U.S.-made models |
| CHIPS and Science Act | Semiconductor subsidies | 15% faster AI system deployment |
| Bipartisan Infrastructure Law | Charging network funding | 82 new fast-charge stations near dealerships |
The White House’s focus on tech independence further accelerated investments. Kia’s 2024 R&D budget includes $900 million for solid-state battery prototypes developed with U.S. universities—a direct response to federal clean energy priorities.
Economic Security and Competitive Strength
National economic resilience increasingly depends on innovative manufacturing strategies. Companies that optimize production networks while addressing environmental concerns gain decisive advantages in global markets. By leveraging cutting-edge technologies and sustainable practices, these organizations not only enhance their operational efficiency but also contribute to a more sustainable future.
For instance, the integration of renewable energy sources into manufacturing processes can significantly reduce carbon footprints, appealing to environmentally conscious consumers. Furthermore, companies that adopt circular economy principles—where waste is minimized and materials are reused—can create additional value while mitigating the risks associated with resource scarcity. This dual focus on innovation and sustainability positions businesses to thrive in a competitive landscape, ensuring they remain agile and responsive to market demands.
Building Resilient Foundations
Robust supply chain practices prevent disruptions that cost U.S. manufacturers $228 billion annually. Automotive leaders now use regional sourcing hubs and AI-driven logistics to maintain production during crises. A 2023 study showed factories with diversified suppliers experienced 43% fewer delays than competitors.
Advanced manufacturing techniques amplify these benefits. 3D-printed components and smart factories reduce waste while boosting output quality. These methods helped one automaker cut defect rates by 37% while using 15% less energy.
| Economic Factor | Traditional Approach | Advanced Strategy |
|---|---|---|
| Supply Chain | Single-source imports | AI-optimized regional networks |
| Manufacturing | Fixed assembly lines | Modular smart factories |
| Energy Use | Fossil fuel reliance | Solar-powered plants |
Climate change policies accelerate this shift. The Biden administration’s $369 billion clean energy investments pushed 78% of manufacturers to adopt emission-reduction targets. Automotive firms leading this charge report 22% higher customer loyalty.
Private sector AI integration proves equally transformative. Machine learning algorithms now predict material shortages 11 weeks in advance, while robotic quality checks ensure 99.8% part accuracy. As one industry analyst noted, “Data-driven production isn’t optional—it’s economic armor.”
These innovations create self-reinforcing cycles. Efficient supply chains lower costs, enabling bigger investments in clean energy infrastructure. This synergy positions forward-thinking companies to dominate next-generation markets while strengthening national economic security.
Advancements in Advanced Manufacturing and AI Integration
Automakers are racing to merge physical production with digital intelligence. Kia now uses digital twin technology to simulate entire factories before construction begins, allowing for precise adjustments in design and workflow. This innovative approach cut prototype development costs by 27% in 2023 while boosting manufacturing capacity.
By creating a virtual model of the production environment, Kia can identify potential bottlenecks and inefficiencies, leading to enhanced operational performance and reduced time-to-market for new vehicles. Additionally, this technology enables real-time monitoring and optimization, ensuring that production lines are adaptable to changing demands and market conditions.
Adoption of Digital Manufacturing Processes
Kia’s Georgia plant employs 3D-printed tooling that adapts to multiple EV models, allowing for greater flexibility in production and reducing the need for extensive retooling. This innovative approach not only streamlines the manufacturing process but also enables rapid prototyping and adjustments based on real-time feedback from the production line.
Real-time sensor networks track supply chain movements across 14 countries, providing valuable data that helps in forecasting demand and managing inventory levels more effectively, thereby reducing parts shortages by 41%. The United Nations Industrial Development Organization reports such systems improve factory output by 19% globally, highlighting the significant impact of integrating advanced technologies in manufacturing operations.
Integration of Artificial Intelligence in Production
Machine learning algorithms predict equipment failures 12 days in advance. One system reduced paint defects by 33% through microscopic quality checks. “AI isn’t replacing workers—it’s amplifying their precision,” notes a production manager at Kia’s Slovakia facility.
Protecting intellectual property grows critical as factories share data across borders. Kia’s blockchain-secured designs prevent unauthorized replication while enabling collaboration with 38 global partners. These innovations demonstrate how smart automation strengthens both economic security and competitive edge.
International Market Expansion and Investment Strategies
Automotive leaders now view cross-border collaboration as essential for survival. Kia’s partnership playbook combines localized production with tech-driven alliances, creating a blueprint for modern global operations.
Strategic Alliances in Key Global Markets
Recent deals with General Motors and European battery startups showcase Kia’s alliance strategy. A 2023 joint venture in Michigan pairs GM’s manufacturing scale with Kia’s EV software expertise. “These partnerships aren’t about sharing costs—they’re about combining superpowers,” explains a Hyundai Motor Group executive.
Policy shifts like the Inflation Reduction Act drive these collaborations. By aligning with U.S.-based firms, Kia secures tax incentives while accessing cutting-edge AI navigation systems. Similar alliances in Germany and China address regional country economic priorities, from carbon neutrality goals to raw material access.
Global Investment and R&D Initiatives
Kia’s $3.1 billion R&D network spans 11 nations, focusing on solid-state batteries and autonomous driving. A Silicon Valley innovation hub works with 27 tech firms to refine vehicle-to-grid energy systems. These investments reinforce its world leading position in patent filings for EV charging solutions.
Robust supply chain coordination enables this global reach. Real-time data sharing with Indonesian nickel miners and Chilean lithium producers prevents bottlenecks. Localized assembly plants then transform these materials into region-specific models, balancing efficiency with market demands.
Overcoming Global Supply Chain Challenges
Global automotive supply chains face unprecedented stress from material shortages to shipping bottlenecks. A 2023 industry report revealed nearly 40% of EV manufacturers experienced delays in battery component deliveries. These disruptions add $2,500 to average vehicle production costs, straining the transportation sector.
The Inflation Reduction Act addresses these issues through localized production incentives. Companies meeting 50% domestic battery material thresholds gain tax credits, accelerating regional supply network development. Kia’s Georgia plant now sources 58% of components within 500 miles, cutting import reliance by 34%.
Three strategies reshape logistics:
- AI-driven demand forecasting slashes excess inventory by 27%
- Blockchain tracking reduces ethical sourcing violations by 41%
- 3D printing hubs near ports trim lead times by 19 days
These innovations help automakers navigate trade uncertainties while meeting percent global emissions targets. As one logistics director noted, “Policy sets the stage, but execution determines who thrives.” With smarter supply chains and IRA alignment, the industry moves toward resilient, cost-effective operations.
Navigating Geopolitical Tensions in the Automotive Sector
Global automotive markets now face unprecedented pressure from shifting power dynamics. The United States and China’s rivalry over electric vehicle dominance has reshaped trade routes, material sourcing, and production strategies. For automakers, balancing these tensions requires agile planning and diversified partnerships.
US-China Competition and Its Implications
Recent tariffs on Chinese battery components forced automakers to rethink supply chain networks. The U.S. now restricts imports of graphite and rare earth metals from China—materials critical for electric vehicles. This move aims to boost domestic production but risks delaying EV adoption timelines.
Three key challenges emerge:
- Chinese companies control 70% of global battery mineral refining
- U.S. incentives under the Inflation Reduction Act favor localized manufacturing
- European Union carbon border taxes complicate transatlantic trade
Automakers face tighter margins as geopolitical risks inflate costs. A 2023 study showed that supply chain disruptions added $1,200 per EV in North America. The European Union offers alternatives through lithium partnerships in Portugal and Spain, reducing reliance on Asian markets.
| Region | EV Policy Focus | Impact |
|---|---|---|
| United States | Local content requirements | +34% domestic battery investment |
| China | Export controls | -19% foreign automaker market share |
| EU | Carbon-neutral supply chains | 41% rise in recycled materials use |
For brands like Kia, success hinges on multi-regional production hubs. Its Georgia plant sources nickel from Canada and lithium from Australia, bypassing Chinese suppliers. As one industry analyst noted, “Geopolitics isn’t just about borders—it’s about who controls the roadmap to electrification.”
Industry Data Insights and Technological Innovation
Automotive leaders now measure success through data-driven innovation and green tech adoption. Recent investments reveal how climate change pressures and market demands reshape priorities, compelling companies to rethink their strategies and embrace sustainability. This shift is evident as manufacturers increasingly focus on electric vehicles (EVs) and renewable energy sources.
The private sector accounts for 83% of clean energy advancements in transportation, with solar panels and battery breakthroughs leading the charge. These innovations not only enhance vehicle performance but also contribute to reducing carbon footprints, demonstrating a commitment to environmental stewardship that resonates with consumers and regulators alike.
R&D Investment and Innovation Metrics
Global automakers poured $127 billion into R&D last year—a 19% increase since 2020. Kia’s $3.5 billion commitment targets solid-state batteries and AI-assisted design tools. These efforts reduced prototype development costs by 31% while accelerating time-to-market.
| Company | R&D Investment (2023) | Key Innovation |
|---|---|---|
| Ford | $8.3B | Lightweight aluminum frames |
| General Motors | $9.1B | Ultium battery platform |
| Kia | $3.5B | 800V charging systems |
Performance Indicators in the Global Market
Three metrics highlight industry shifts:
- EV sales grew 54% worldwide in 2023, outpacing traditional vehicles
- Advanced manufacturing techniques cut production waste by 28%
- Solar panel installations at factories increased 600% since 2018
These trends reflect tighter emissions regulations and consumer eco-consciousness. As one analyst noted, “Companies blending tech innovation with sustainability will dominate the next decade.” With $22 billion in global market investments for 2024, the race to lead clean energy mobility intensifies.
Commitment to Sustainability and Climate Initiatives
Automakers face a critical challenge: reducing environmental impact without sacrificing growth. Kia tackles this through circular manufacturing systems that reuse 95% of production waste. Its Georgia plant now operates on 40% solar energy, while European facilities use recycled aluminum for 78% of chassis components.
Eco-friendly Manufacturing Processes
Kia redesigned factories to slash water use by 58% since 2020. Advanced filtration systems treat and reuse coolant fluids, while AI optimizes paint application to minimize overspray. “Every bolt and bracket gets a second life,” explains a production manager at their Slovakia facility.
Recent years saw bold shifts in material sourcing. The company partners with 14 suppliers certified by the Global Recycling Standard, ensuring ethical practices across its global supply network. Battery casings now contain 32% post-industrial scrap metal, cutting mining demands.
Clean Energy and Climate Change Strategies
A $2.7 billion investment funds wind farms in Texas and solar arrays near Seoul. These projects will power 600,000 homes annually while offsetting 38% of Kia’s operational emissions by 2026. Machine learning algorithms track energy consumption patterns, reducing factory power waste by 19%.
Intellectual property protections safeguard these innovations. A director at the National Renewable Energy Lab states: “Kia’s battery recycling patents could rewrite EV sustainability rules.” Policy announcements like the U.S.-South Korea Clean Energy Partnership promise faster adoption of these breakthroughs.
Through smart grids and AI-driven logistics, Kia proves environmental responsibility fuels business success. As climate regulations tighten, its dual focus on clean energy and closed-loop systems positions it as an industry pacesetter.
Corporate Leadership and Future Outlook
Corporate leadership faces a dual challenge in the modern automotive landscape: steering legacy giants while fostering agile newcomers. Traditional chaebols now collaborate with tech start-ups to accelerate innovation. Hyundai’s $900 million venture fund, for example, backs 23 AI-driven mobility firms worldwide.
Balancing Scale and Agility
Expanding manufacturing capacity without compromising quality remains critical. Kia’s Georgia plant uses modular assembly lines that switch between EV models in 90 minutes—a system developed with Silicon Valley robotics start-ups. This hybrid approach cuts downtime by 37% compared to traditional factories.
| Challenge | Traditional Approach | Modern Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Tech Integration | In-house R&D | Start-up partnerships |
| Quality Control | Manual inspections | AI defect detection |
| Supply Chain Ethics | Third-party audits | Blockchain tracking |
The European Union and United Nations now set stringent benchmarks for ethical sourcing. Over 68% of automakers report these policies directly influence partner selection. Kia’s recent alliance with a Norwegian battery recycler aligns with UN Sustainable Development Goal 12.
Emerging country economic priorities further shape strategies. Investments in India’s EV infrastructure and Brazil’s lithium reserves position leaders for world leading market access. As one executive noted, “Initiatives we announced would determine whether we lead revolutions or chase them.”
The automotive sector must also address talent gaps. Cross-training programs in AI and renewable energy prepare workforces for next-gen factories. With global EV demand projected to triple by 2030, adaptable leadership separates industry pioneers from followers.
Conclusion
Strategic vision transformed an underdog automaker into an industry pacesetter. By aligning policy incentives with localized battery production and advanced manufacturing, Kia reshaped its role in the transportation sector. Billions of dollars in R&D fueled breakthroughs like 800-volt charging systems and AI-driven supply networks.
Three pillars sustain this momentum: controlling critical mineral supplies, optimizing regional production hubs, and scaling next-generation EV technology. The company’s 6% U.S. market share reflects its ability to balance innovation with affordability—a formula tested during supply chain crises.
Future success hinges on securing ethical mineral sources for million EVs while maintaining cost leadership. Investments in solid-state batteries and recycled materials will define competitiveness as global demand surges. Partnerships with tech firms and universities ensure access to emerging innovations.
Kia’s journey proves that agility trumps scale in volatile markets. With 70% domestic battery sourcing and factories spanning three continents, it stands ready to influence the world automotive landscape. Sustaining dominance now requires doubling down on what worked: marrying policy awareness with engineering excellence.
FAQ
▶
▶
▶
▶
▶
▶
▶
▶
▶
▶