The global automotive industry stands at a pivotal crossroads, with traditional powerhouses like the United States and Germany competing for dominance while facing unprecedented challenges from emerging markets and technological disruption. This comprehensive analysis examines how these two automotive giants compare across ten critical dimensions, from historical foundations to future strategies, providing a data-driven assessment of their respective positions in global automotive industry leadership.
1. Automotive Ecosystem Overview
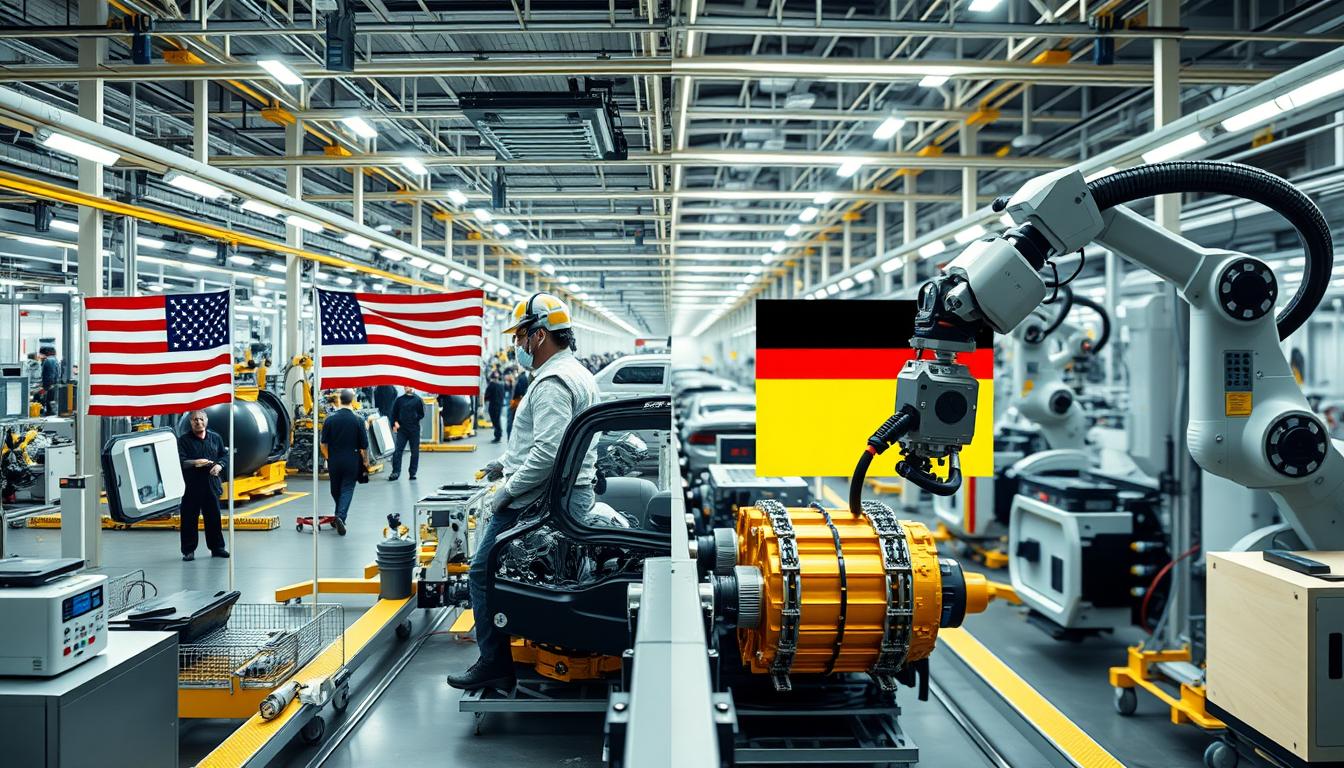
Modern manufacturing facilities showcase the technological advancement in both US and German automotive production
The United States and Germany have developed distinct automotive ecosystems shaped by their unique historical trajectories and industrial philosophies. The American automotive industry, pioneered by Henry Ford’s revolutionary assembly line techniques, has historically emphasized mass production, scale economies, and market accessibility. In contrast, Germany’s automotive sector evolved with a stronger focus on engineering precision, technical innovation, and premium quality.
United States Automotive Landscape
The US automotive industry contributes approximately 3% to the national GDP and employs over 1.7 million people directly, with millions more in related industries. Major American automakers include General Motors, Ford Motor Company, and Tesla, with the latter disrupting traditional manufacturing paradigms through its focus on electric vehicles and technological integration.
German Automotive Landscape
Germany’s automotive sector represents approximately 5% of the country’s GDP and employs around 830,000 people directly. The industry is anchored by global powerhouses including Volkswagen Group, BMW, and Mercedes-Benz, all of which have cultivated strong reputations for engineering excellence and premium quality across international markets.
2. Core Strengths and Areas of Specialization

United States Strengths
- Mass production efficiency and economies of scale
- Dominance in pickup trucks and large SUV segments
- Software integration and tech ecosystem development
- Electric vehicle startup innovation (Tesla, Rivian)
- Autonomous driving technology advancement
German Strengths
- Precision engineering and manufacturing quality
- Luxury vehicle segment leadership
- Drivetrain and mechanical innovation
- Advanced materials application
- Manufacturing process optimization
The contrast in specialization reflects deeper industrial philosophies: American manufacturers have historically prioritized production volume and market accessibility, while German automakers have emphasized engineering precision and brand prestige. These different approaches continue to influence their global strategies and market positioning today.
3. Automotive Brands and Global Influence
Brand Value and Global Recognition
| Brand | Country | Global Brand Value (2023) | Key Markets | Brand Positioning |
| Tesla | United States | $66.2 billion | North America, China, Europe | Electric innovation, technology |
| Mercedes-Benz | Germany | $58.8 billion | Europe, China, North America | Luxury, engineering excellence |
| BMW | Germany | $46.3 billion | Europe, China, North America | Performance luxury, driving dynamics |
| Toyota* | Japan | $64.5 billion | Global presence | Reliability, value |
| Ford | United States | $20.3 billion | North America, Europe | Accessibility, utility |
| Volkswagen | Germany | $40.0 billion | Europe, China, South America | Practical engineering, value |
*Included for reference as global market leader
German brands have successfully cultivated premium positioning across global markets, with Mercedes-Benz and BMW consistently ranking among the world’s most valuable automotive brands. American manufacturers demonstrate greater diversity in positioning, with Tesla establishing itself as a technology-focused premium brand while Ford and GM maintain stronger positions in mass-market segments.
5. Innovation, R&D, and Technology Leadership

R&D Investment Comparison
German automakers demonstrate exceptional commitment to research and development, with Volkswagen Group investing approximately €15.6 billion annually (5.5% of revenue), while BMW and Mercedes-Benz allocate 5.7% and 5.4% of revenue respectively. American manufacturers show more variation, with Tesla investing approximately 4.1% of revenue in R&D, General Motors 5.0%, and Ford 4.2%.
Patent Activity and Innovation Focus
United States Innovation Focus
- Software integration and user experience
- Battery technology and energy density
- Autonomous driving systems
- Vehicle connectivity and IoT integration
- Manufacturing automation
German Innovation Focus
- Drivetrain efficiency and performance
- Advanced materials and lightweight construction
- Safety systems and driver assistance
- Manufacturing process optimization
- Hydrogen fuel cell development
6. Sustainability and Environmental Standards

Emissions Reduction Approaches
The regulatory environments in the United States and Germany have shaped distinctly different approaches to emissions reduction. The European Union’s stringent CO2 targets (average 95g/km across manufacturer fleets) have driven German automakers toward comprehensive electrification strategies, with Volkswagen Group committing €89 billion to electric vehicle development through 2026.
The United States has pursued a more varied approach, with California’s zero-emission vehicle mandates driving regional compliance while federal standards have fluctuated with political administrations. This regulatory environment has created a bifurcated market where Tesla has pursued aggressive electrification while traditional American manufacturers have maintained substantial internal combustion engine production alongside growing electric offerings.
Electrification Strategies Comparison
| Manufacturer | Country | EV Investment (Billions) | EV Models (2024) | Carbon Neutrality Target |
| Volkswagen Group | Germany | €89 | 20 | 2050 |
| Mercedes-Benz | Germany | €60 | 10 | 2039 |
| BMW | Germany | €30 | 13 | 2050 |
| General Motors | United States | $35 | 13 | 2040 |
| Ford | United States | $50 | 9 | 2050 |
| Tesla | United States | $10+ | 5 | Not specified |
7. Financial Performance and Economic Impact
Revenue and Profitability
German manufacturers have generally maintained stronger profit margins, particularly in the premium segment where BMW and Mercedes-Benz consistently achieve operating margins between 8-12%. Volkswagen Group’s scale enables it to generate the highest absolute revenue among all global automakers at approximately €279.2 billion (2023).
American manufacturers show greater variation in financial performance. Tesla has achieved industry-leading operating margins exceeding 15% during peak periods, though these have moderated with increased competition. Traditional American manufacturers have struggled with lower margins, with General Motors and Ford typically achieving 5-8% operating margins, though their truck and SUV segments perform substantially better.
Economic Contribution
The automotive industry represents a critical economic pillar for both nations. In Germany, the sector accounts for approximately 5% of GDP and generates export value exceeding €300 billion annually. The United States automotive industry contributes approximately 3% to national GDP with a trade deficit in finished vehicles but strength in parts manufacturing and technology development.
8. Supply Chain and Manufacturing Efficiency
Supply Chain Strategies
German manufacturers have historically maintained closer geographic integration with their supplier networks, with approximately 75% of components for German-assembled vehicles sourced from within the European Union. This proximity has facilitated the just-in-time manufacturing model while reducing logistics costs and carbon footprint.
American manufacturers have developed more globally distributed supply chains, with significant reliance on components from Mexico, China, and Southeast Asia. This approach has optimized cost structures but introduced greater vulnerability to supply chain disruptions, as evidenced during recent semiconductor shortages and pandemic-related logistics challenges.
Manufacturing Efficiency Comparison
United States Manufacturing Approach
- Large-scale production facilities
- Higher automation in assembly processes
- Flexible manufacturing platforms
- Distributed global production network
- Emphasis on production volume
German Manufacturing Approach
- Precision-focused production systems
- Higher worker specialization
- Integrated quality control processes
- Regional production concentration
- Emphasis on production quality
9. Global Partnerships and Production Facilities Abroad
International Manufacturing Footprint
German automakers have established significant manufacturing presence in key markets, with Volkswagen Group operating more than 120 production facilities across 30+ countries. BMW and Mercedes-Benz have strategically located production in their largest markets, including the United States and China, allowing them to mitigate currency fluctuations and trade barriers while adapting products to local preferences.
American manufacturers have pursued different internationalization strategies. General Motors maintains substantial global manufacturing operations despite scaling back from its previous global footprint. Ford has consolidated around regional production hubs in North America, Europe, and Asia. Tesla has pursued a focused strategy of building gigafactories in key markets (United States, China, Germany) to serve regional demand while maintaining economies of scale.
Strategic Alliances
Cross-border partnerships have become increasingly important as manufacturers navigate the capital-intensive transition to electrification and autonomous driving. German manufacturers have formed strategic technology alliances, exemplified by BMW and Mercedes-Benz’s joint development of autonomous driving systems and Volkswagen’s partnerships with Ford on commercial vehicles and electric platforms.
American manufacturers have pursued technology-focused partnerships, with General Motors collaborating with Honda on electric vehicle development and Ford partnering with Volkswagen on commercial vehicles and EV platforms. Tesla has maintained a more independent approach while selectively partnering with suppliers for battery technology and manufacturing processes.
10. Challenges and Future Outlook

Common Challenges
Opportunities
- Growing global demand for electric vehicles
- Software-defined vehicle revenue streams
- Autonomous driving commercialization
- Sustainability-driven innovation
- New mobility business models
Challenges
- Intensifying Chinese competition
- Battery supply chain constraints
- Semiconductor availability
- Regulatory complexity and compliance costs
- Workforce transition to new skill requirements
Strategic Responses
German manufacturers are pursuing strategic realignment around electrification while protecting their traditional strengths in engineering excellence and premium positioning. This includes substantial investments in battery technology, software development capabilities, and manufacturing transformation while maintaining their core brand identities.
American manufacturers demonstrate greater strategic divergence. Tesla continues its technology-focused growth strategy while expanding into energy systems and robotics. Traditional manufacturers like General Motors and Ford are pursuing parallel strategies that maintain their internal combustion engine strengths while accelerating electric vehicle development through dedicated platforms and sub-brands.
Policy Environment
Government policy will significantly influence competitive dynamics. The European Union’s regulatory framework provides clear long-term direction with its 2035 phase-out of internal combustion engine vehicles, creating a stable but demanding environment for German manufacturers. The United States policy landscape offers substantial financial incentives through the Inflation Reduction Act but with greater political uncertainty regarding long-term regulatory direction.
Conclusion: Complementary Leadership in a Transforming Industry
The analysis across these ten dimensions reveals that the United States and Germany demonstrate complementary forms of leadership in the global automotive industry. German manufacturers maintain advantages in engineering precision, manufacturing quality, and premium brand positioning. American manufacturers demonstrate strengths in technology integration, electric vehicle innovation, and software development.
Rather than a single leader emerging, the global automotive industry appears to be evolving toward a more complex competitive landscape where different forms of leadership coexist. The most successful manufacturers will likely be those that can integrate the engineering excellence traditionally associated with German automakers with the technological innovation and software capabilities where American manufacturers have shown strength.
As the industry navigates its most profound transformation in a century, both American and German manufacturers face the challenge of leveraging their respective strengths while addressing structural weaknesses. Their success in this transition will determine whether they can maintain leadership positions against emerging competitors, particularly from China, in the rapidly evolving global automotive landscape.