The hybrid car race has intensified as automakers compete to develop the most efficient, innovative, and appealing electrified vehicles. Nissan and Hyundai have emerged as significant contenders in this space, each bringing unique approaches to hybrid technology. This comprehensive comparison examines how these automotive giants stack up against each other in the increasingly competitive hybrid market, analyzing everything from their technological innovations to market performance and future strategies.
Company Background and Hybrid Development
Nissan’s Yokohama headquarters (left) and Hyundai’s Seoul headquarters (right) represent the different cultural approaches to automotive innovation
Founded in 1933, Nissan Motor Company emerged from the shadows of post-war Japan to become a global automotive powerhouse. The company’s journey into hybrid technology began in earnest during the early 2000s, though their initial focus leaned heavily toward all-electric vehicles with the pioneering Leaf. Nissan’s approach to electrification has been methodical, developing their e-Power hybrid system as a bridge technology while continuing to advance their EV capabilities.
Hyundai Motor Company, established in 1967 in South Korea, represents a more recent success story in the automotive world. Initially focused on building affordable vehicles for the domestic market, Hyundai has transformed into a global brand known for value, quality, and increasingly, technological innovation. Their hybrid journey began in the late 2000s, with the company making significant investments in diverse electrification technologies including hybrid, plug-in hybrid, and hydrogen fuel cell vehicles.
Both companies have approached the hybrid car race with different philosophies. Nissan initially prioritized all-electric technology before developing hybrid systems, while Hyundai embraced a parallel development strategy across multiple electrification technologies. These foundational differences continue to influence their current hybrid offerings and market positioning in the competitive automotive landscape, where hybrid power and performance on the track are crucial for drivers and teams alike.
Core Business and Hybrid Focus
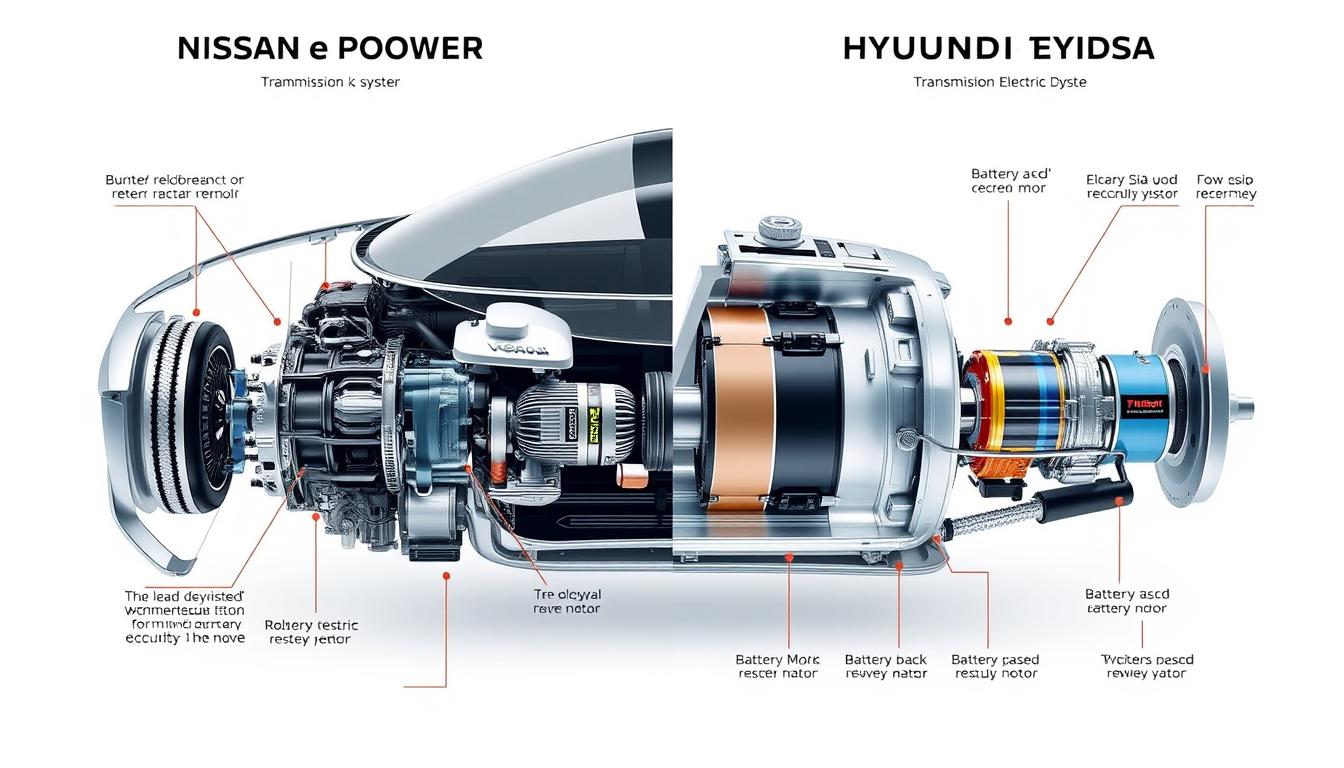
Technical comparison of Nissan’s e-Power and Hyundai’s TMED hybrid systems showing fundamental design differences
Nissan’s hybrid strategy centers around their innovative e-Power system, which differs significantly from conventional hybrid setups. In e-Power vehicles, the gasoline engine functions solely as a generator to produce electricity, while the electric motor exclusively drives the wheels. This series hybrid approach aims to deliver EV-like driving experiences with the convenience of gasoline refueling, featured in models like the Note e-Power and Qashqai e-Power.
Hyundai has developed a more diverse hybrid portfolio using their Transmission-Mounted Electric Device (TMED) system. This parallel hybrid configuration integrates the electric motor with a conventional transmission, allowing both the engine and motor to power the wheels directly. This technology underpins popular models like the Sonata Hybrid, Tucson Hybrid, and the dedicated Ioniq Hybrid platform, which was specifically designed for electrified powertrains.
| Feature | Nissan Hybrid Approach | Hyundai Hybrid Approach |
| Primary System | e-Power (Series Hybrid) | TMED (Parallel Hybrid) |
| Power Delivery | Electric motor drives wheels exclusively | Both engine and motor can drive wheels |
| Engine Function | Generator only | Direct propulsion + charging |
| Flagship Models | Note e-Power, Qashqai e-Power | Sonata Hybrid, Tucson Hybrid, Ioniq |
| Development Priority | EV-like driving experience | Efficiency and versatility |
Nissan’s R&D priorities have focused on refining the e-Power system to improve efficiency and reduce costs, while maintaining the distinctive EV-like driving characteristics. Hyundai has invested heavily in making hybrid technology available across more vehicle segments, from compact cars to SUVs, while simultaneously developing their dedicated IONIQ sub-brand for fully electric vehicles.
Strengths and Weaknesses Analysis

Fuel efficiency testing reveals real-world performance differences between Nissan and Hyundai hybrid technologies
Nissan Strengths
- e-Power system delivers smoother, more EV-like acceleration
- Simpler mechanical design with fewer transmission components
- Strong urban fuel efficiency due to optimized generator operation
- More consistent driving experience across varying conditions
- Leverages EV development expertise from Leaf program
Nissan Weaknesses
- Limited hybrid model selection compared to competitors
- Higher system complexity for maintenance and repairs
- Less efficient at highway speeds than parallel hybrids
- Higher initial production costs affecting vehicle pricing
- Late market entry compared to hybrid pioneers
Hyundai Strengths
- Broader hybrid model lineup across multiple segments
- Excellent highway fuel efficiency with direct engine drive
- Competitive pricing with strong value proposition
- Industry-leading warranty coverage (10-year/100,000-mile powertrain)
- Innovative design aesthetics attracting younger buyers
Hyundai Weaknesses
- Less refined electric-only operation than series hybrids
- More complex transmission systems with potential reliability concerns
- Slightly lower urban fuel efficiency in some models
- Inconsistent availability across global markets
- Brand perception still catching up to Japanese competitors
In terms of technology, Nissan’s e-Power system excels in delivering a more electric-like driving experience with instant torque and smoother acceleration. However, Hyundai’s parallel hybrid system typically achieves better highway fuel efficiency where steady-state operation benefits from direct engine drive. Nissan’s approach simplifies the transmission but adds complexity to the electrical systems, while Hyundai’s conventional transmission with integrated motor offers familiar driving dynamics but with more mechanical components.
Design aesthetics present another contrast, with Nissan adopting a more conservative approach that emphasizes continuity with their conventional models. Hyundai has embraced more distinctive styling for their hybrids, particularly with the dedicated Ioniq platform, helping them stand out in a crowded market. This design-forward approach has helped Hyundai attract younger buyers to their hybrid offerings, which are increasingly important in the racing era of cars where hybrid power and advanced software play a critical role in performance. As competition heats up on the road, the amount of horsepower and braking efficiency in these vehicles becomes essential for drivers looking to excel in this automotive race.
Innovation and Technology

Battery technology comparison reveals different approaches to energy density, thermal management, and longevity
The technological battle between Nissan and Hyundai extends beyond their basic hybrid architectures to encompass battery technology, powertrain efficiency, and software integration. Nissan has focused on optimizing their lithium-ion battery packs for power density rather than energy storage, consistent with the e-Power system’s need for quick power delivery rather than extended electric-only range. Their variable compression ratio engine technology, when paired with e-Power, represents a significant innovation in optimizing generator efficiency.
Hyundai has invested heavily in next-generation battery chemistry, including the development of solid-state batteries through partnerships with leading battery manufacturers. Their hybrid systems utilize more conventional lithium-ion technology currently, but with sophisticated thermal management systems that have demonstrated excellent longevity in real-world usage. Hyundai’s Active Shift Control technology, which uses the electric motor to precisely control transmission shifts, represents an innovative approach to improving efficiency and driving refinement.
Nissan’s Key Innovations
- Variable Compression Technology: Adjusts engine compression ratio on the fly for optimal efficiency
- e-Pedal Step: One-pedal driving capability for enhanced urban efficiency
- Lightweight Inverter Design: Reduces system weight while improving power density
Hyundai’s Key Innovations
- Active Shift Control: Uses motor to precisely control transmission shifts
- Predictive Energy Management: Uses navigation data to optimize hybrid operation
- Solar Roof Integration: Supplemental charging through roof-mounted solar panels
Software integration represents another battleground, with both manufacturers developing increasingly sophisticated energy management systems. Hyundai’s predictive energy management system uses navigation data to anticipate road conditions and optimize hybrid operation accordingly. Nissan has focused on refining their e-Pedal technology, which enables one-pedal driving in urban environments while maximizing energy recuperation.
Autonomous driving features are increasingly integrated with hybrid powertrains, with both companies developing systems that optimize efficiency based on driving conditions. Nissan’s ProPILOT system and Hyundai’s Highway Driving Assist both incorporate adaptive cruise control and lane-keeping functions that can reduce energy consumption through smoother operation than typical human driving.

Research and development facilities where next-generation hybrid technologies are being perfected
Sustainability and Environmental Initiatives

Eco-friendly manufacturing facilities demonstrate both companies’ commitment to sustainable production
Beyond the direct emissions benefits of their hybrid vehicles, both Nissan and Hyundai have implemented comprehensive sustainability initiatives throughout their operations. Nissan’s Green Program 2022 established targets for reducing carbon dioxide emissions from corporate activities by 30% compared to 2005 levels. Their manufacturing facilities in Japan, the UK, and the US have implemented significant renewable energy installations, with the Sunderland, UK plant operating with 10 wind turbines generating 6.6MW of power.
Hyundai’s Strategy 2025 includes ambitious targets for carbon neutrality, with plans to achieve carbon neutrality in all operational aspects by 2045. Their manufacturing facilities increasingly utilize renewable energy, with their Asan plant in South Korea featuring a 13MW solar installation. Hyundai has also pioneered the use of recycled ocean plastic in interior components for several hybrid models, demonstrating their commitment to circular economy principles.
Lifecycle Carbon Footprint Comparison
Independent lifecycle assessments indicate that Hyundai’s manufacturing processes for hybrid vehicles currently produce approximately 12% lower carbon emissions than industry averages, while Nissan achieves approximately 9% reduction. However, when considering the entire lifecycle including vehicle use, Nissan’s e-Power system demonstrates marginally better overall carbon reduction due to its optimized urban efficiency where many vehicles spend most of their operational lives.
Battery recycling represents a critical aspect of hybrid vehicle sustainability. Nissan has established partnerships with recycling specialists to recover up to 98% of materials from their battery packs. Hyundai has developed their own proprietary recycling technology that enables the recovery of rare earth elements from used batteries with minimal environmental impact, though this technology is still being scaled to production levels.
Both manufacturers have committed to sustainable supply chains, with increasing scrutiny of raw material sourcing for battery components. Hyundai has been particularly proactive in establishing transparent supply chain verification for cobalt and lithium, while Nissan has focused on reducing dependency on rare earth elements through alternative motor designs.
Financial Performance in Hybrid Segment
Financial performance metrics reveal different investment strategies and revenue growth patterns
The financial aspects of hybrid vehicle development and sales reveal significant differences in approach between the two manufacturers. Nissan has invested approximately $4.3 billion in hybrid technology development since 2018, with a particular focus on refining their e-Power system and reducing production costs. This investment represents approximately 23% of their total R&D budget during this period, reflecting a significant but measured commitment to hybrid technology.
Hyundai has been more aggressive in their hybrid investments, allocating approximately $5.8 billion to hybrid technology development since 2018, representing nearly 31% of their total R&D expenditure. This higher proportional investment reflects Hyundai’s strategy of rapid hybrid portfolio expansion across multiple vehicle segments and price points.
| Financial Metric | Nissan | Hyundai |
| Hybrid R&D Investment (2018-2023) | $4.3 billion | $5.8 billion |
| Hybrid Revenue Growth (2021-2023) | 17% annual | 23% annual |
| Profit Margin on Hybrid Models | 8.3% average | 7.6% average |
| Manufacturing Cost Reduction (2020-2023) | 14% | 18% |
Revenue growth from hybrid vehicle sales shows Hyundai outpacing Nissan, with 23% annual growth compared to Nissan’s 17%. However, Nissan maintains slightly higher profit margins on their hybrid models at approximately 8.3% compared to Hyundai’s 7.6%. This difference reflects Nissan’s more premium positioning of their e-Power technology versus Hyundai’s volume-focused approach.
Both manufacturers have achieved significant manufacturing cost reductions for their hybrid systems, with Hyundai reducing costs by approximately 18% between 2020 and 2023, compared to Nissan’s 14% reduction. These improvements have been critical in maintaining competitiveness as hybrid technology becomes increasingly mainstream and price-sensitive.
Brand Image and Customer Loyalty
Customer satisfaction metrics reveal strengths and weaknesses in brand perception among hybrid owners
Brand perception plays a crucial role in hybrid vehicle purchasing decisions, with reliability, innovation, and environmental credentials all influencing consumer choices. Nissan has leveraged their pioneering position in electric vehicles to build credibility for their hybrid offerings, with consumer surveys indicating strong association between Nissan and electrification technology. Their overall brand perception scores for hybrid vehicles average 7.8 out of 10 in major markets.
Hyundai has successfully transformed their brand image from budget-focused to technology-forward, with their hybrid vehicles playing a key role in this evolution. Consumer perception surveys show Hyundai scoring particularly well on value for money (8.4/10) and warranty coverage (9.1/10), with an overall hybrid brand perception score of 8.1 out of 10.
“Hyundai has successfully positioned their hybrid vehicles as both technologically advanced and accessible, while Nissan’s e-Power system is perceived as more premium but with a stronger connection to pure electric driving experiences.”
Customer loyalty metrics reveal interesting patterns, with Nissan hybrid owners showing 67% brand loyalty for their next vehicle purchase, compared to Hyundai’s 72%. However, when specifically considering hybrid-to-hybrid loyalty, Nissan performs better with 83% of e-Power owners planning to purchase another hybrid, compared to 78% of Hyundai hybrid owners.
After-sales support represents another differentiating factor, with Hyundai’s industry-leading 10-year/100,000-mile powertrain warranty providing significant peace of mind for hybrid purchasers concerned about battery longevity. Nissan offers more standard warranty coverage of 5-years/60,000-miles for their hybrid components, though this is supplemented by strong dealer service ratings averaging 4.2/5 across major markets.
Challenges and Future Prospects

Concept designs hint at the future direction of hybrid technology for both manufacturers
Both Nissan and Hyundai face significant challenges in the rapidly evolving automotive landscape. The accelerating transition to fully electric vehicles presents perhaps the most significant challenge, with some markets announcing future bans on internal combustion engines that will eventually impact hybrid vehicles. Nissan’s Ambition 2030 plan acknowledges this transition, positioning e-Power as a bridging technology while expanding their pure electric offerings.
Hyundai’s Strategy 2025 similarly balances hybrid and electric development, with plans to offer 44 electrified models by 2025, including 23 battery electric vehicles. Their hybrid technology development continues in parallel with electric vehicle advancement, with particular focus on plug-in hybrid technology as a transitional solution for markets with limited charging infrastructure.
Regulatory Landscape Impact
Evolving emissions regulations present both challenges and opportunities. The EU’s increasingly stringent CO2 targets for 2025 and 2030 will require continued advancement in hybrid efficiency, while China’s dual-credit policy system incentivizes both hybrid and electric vehicle production. In the US, the restoration of stricter CAFE standards has renewed the importance of fuel-efficient hybrid options across manufacturer lineups.
Technological roadmaps reveal diverging approaches to future hybrid development. Nissan is exploring the integration of solid-state battery technology with their e-Power system, potentially offering significantly improved power density and faster charging capabilities. Their next-generation e-Power system, expected around 2025, aims to reduce system cost by 30% while improving efficiency by 20%.
Hyundai is developing more integrated hybrid/plug-in hybrid architectures that can share components with their electric vehicles, creating manufacturing efficiencies and cost reductions. Their next-generation hybrid system, expected to debut in 2024, will feature increased electrification with 48-volt systems becoming standard across more of their lineup.

Research and development continues as both companies refine their hybrid technologies
Conclusion: Who Leads the Hybrid Car Race?
The hybrid car race between Nissan and Hyundai reveals two manufacturers with different approaches but similar goals. Hyundai has established a stronger market position through their broader model lineup, aggressive pricing, and industry-leading warranty coverage. Their parallel hybrid system offers excellent highway efficiency and familiar driving dynamics that have resonated with mainstream consumers.
Nissan’s more innovative e-Power system delivers a distinctive driving experience that bridges the gap between hybrid and electric vehicles. While their market share lags behind Hyundai’s in most regions, their technology shows promise for urban-focused drivers and those seeking an electric-like experience without charging infrastructure concerns.
Looking ahead, both manufacturers face the challenge of balancing hybrid development with the transition to fully electric vehicles. Hyundai appears better positioned for near-term growth with their diverse hybrid lineup and strong market momentum, while Nissan’s technological approach may offer advantages as consumer preferences continue to evolve toward electrification.
The ultimate winner in this hybrid car race will likely be determined not just by technology or market share, but by which manufacturer most effectively uses hybrid vehicles as a stepping stone in the broader transition to sustainable mobility.
Experience the Hybrid Difference Yourself
The best way to understand the unique characteristics of Nissan’s e-Power and Hyundai’s hybrid systems is through a personal test drive. Schedule a comparison drive today to experience both technologies and determine which better suits your driving needs.