The race to develop advanced artificial intelligence is reshaping our technological landscape, with OpenAI and Anthropic emerging as two of the most influential players. Both companies are pushing the boundaries of what AI can achieve, but they approach this challenge with distinct philosophies, research methodologies, and ethical frameworks. This comprehensive comparison examines these AI pioneers across ten critical dimensions to understand who might lead the next generation of artificial intelligence development.
Company Profiles and Philosophies
OpenAI was founded in 2015 by Sam Altman, Greg Brockman, Elon Musk, and others as a non-profit research laboratory. Its mission statement is clear: “to ensure that artificial general intelligence benefits all of humanity.” Initially committed to open-source principles, the organization later adopted a “capped-profit” model to attract the capital needed for large-scale AI development while maintaining its alignment with beneficial outcomes.
Under CEO Sam Altman’s leadership, OpenAI has pursued a strategy of developing increasingly capable general-purpose AI systems. Their philosophy centers on the responsible democratization of AI technology, balancing innovation with safety considerations. This approach has led to the development of models like GPT-4, which are designed to be versatile across numerous applications.
Anthropic, founded in 2021 by former OpenAI researchers including Dario and Daniela Amodei, positions itself as an AI safety company first and foremost. Their mission focuses on building “reliable, interpretable, and steerable AI systems.” This safety-first philosophy stems from concerns about the direction of AI development at larger organizations.
Anthropic’s constitutional AI approach embeds ethical guidelines directly into their models’ training process. This reflects their core belief that as AI systems become more powerful, their alignment with human values becomes increasingly critical. While both companies share concerns about AI safety, Anthropic places this consideration at the center of its identity and development methodology.
Core Specializations and Research Focus
OpenAI has developed a diverse portfolio of AI models and technologies. Their flagship GPT (Generative Pre-trained Transformer) series has evolved through multiple iterations, with GPT-4 representing their most advanced language model to date. Beyond text generation, OpenAI has created DALL·E for image generation, Codex for code completion, and ChatGPT as a conversational interface to their underlying models.
Their research spans multiple domains including reinforcement learning from human feedback (RLHF), multimodal capabilities, and scaling laws for neural language models. OpenAI’s approach often involves building general-purpose systems that can be fine-tuned for specific applications, reflecting their belief in the value of artificial general intelligence (AGI).
Anthropic has focused more narrowly on developing their Claude AI assistant and the underlying constitutional AI framework. Their research emphasizes AI alignment—ensuring AI systems act in accordance with human values and intentions. This includes work on mechanistic interpretability (understanding how models work internally), constitutional AI (training models to follow principles), and harmlessness (preventing models from generating harmful outputs).
While OpenAI explores the frontiers of what AI can do across multiple domains, Anthropic concentrates on making AI systems more reliable, transparent, and aligned with human values. This difference in research focus reflects their distinct approaches to advancing artificial intelligence technology.
Strengths and Weaknesses
OpenAI Strengths
- Technical leadership in scaling language models
- Diverse product ecosystem (text, code, images, audio)
- Strong commercial adoption and brand recognition
- Robust infrastructure for model deployment
- Significant financial backing from Microsoft
OpenAI Weaknesses
- Criticism over commercialization pace versus safety
- Governance challenges and leadership tensions
- Less transparent research publication in recent years
- Concerns about model hallucinations and reliability
- Dependency on Microsoft partnership
Anthropic Strengths
- Industry-leading safety protocols and alignment
- Constitutional AI approach for ethical guardrails
- Larger context windows in Claude models
- Transparent research publication practices
- Strong focus on reducing model hallucinations
Anthropic Weaknesses
- Narrower product ecosystem than competitors
- Limited multimodal capabilities (primarily text)
- Smaller scale of deployment and user base
- Less developed enterprise integration options
- Newer entrant with less established market position
Both companies demonstrate distinct strengths and face unique challenges. OpenAI excels in technical innovation and commercial reach but faces questions about its governance and safety practices. Anthropic leads in safety research and alignment techniques but has a more limited product range and market presence. These differences reflect their contrasting priorities and development philosophies.
Market Reach and Ecosystem Integration
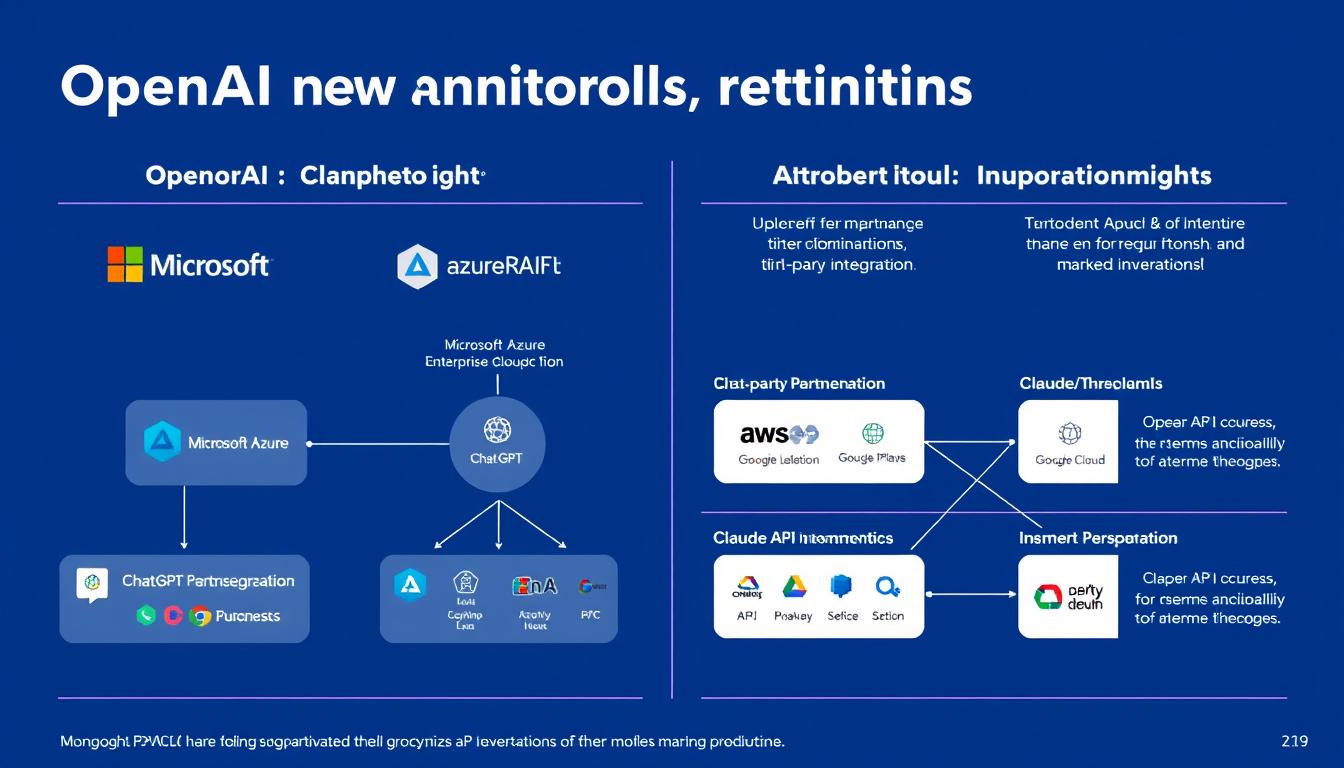
OpenAI has achieved remarkable market penetration through its flagship product ChatGPT, which reached 100 million users faster than any consumer application in history. Their API services power thousands of applications across industries, while their partnership with Microsoft has integrated OpenAI’s technology into products like Bing, Office 365, and GitHub Copilot.
The OpenAI ecosystem includes developer tools, plugins, and enterprise solutions that have been adopted by organizations ranging from startups to Fortune 500 companies. Their models support a wide range of use cases including content generation, customer service, code assistance, and creative applications.
Anthropic has taken a more measured approach to market expansion, focusing initially on select enterprise partnerships. Their Claude AI assistant is available through their API and has been integrated with platforms like Quora’s Poe, Notion, and various specialized business applications. Anthropic has secured strategic partnerships with companies including Google, Amazon, and Salesforce.
While Anthropic’s market footprint is smaller than OpenAI’s, they have positioned Claude as a premium option for enterprises with strict requirements for safety, reliability, and data handling. Their selective approach to partnerships reflects their emphasis on responsible deployment over rapid scaling.
| Integration Feature | OpenAI | Anthropic |
| Primary Cloud Partner | Microsoft Azure | AWS & Google Cloud |
| API Availability | Widespread with tiered access | Selective with emphasis on enterprise |
| Consumer Product | ChatGPT (Free & Plus) | Claude (Free & Pro) |
| Enterprise Solution | ChatGPT Enterprise | Claude Enterprise |
| Third-party Integrations | Extensive ecosystem | Growing selectively |
Innovation and Technological Edge
OpenAI has consistently pushed the boundaries of AI capabilities through scale and architectural innovations. GPT-4 demonstrated significant improvements in reasoning, factuality, and multimodal understanding compared to its predecessors. Their DALL·E models have advanced the state of image generation, while their CLIP system effectively bridges text and visual understanding.
OpenAI’s innovations include pioneering work on reinforcement learning from human feedback (RLHF), which has become an industry standard for aligning AI systems with human preferences. They’ve also made breakthroughs in efficient fine-tuning methods and multimodal training techniques.
Anthropic has focused its innovation efforts on developing more reliable and interpretable AI systems. Their constitutional AI approach represents a novel method for training models to follow principles rather than simply mimicking patterns in data. Claude models feature enhanced capabilities for following complex instructions and maintaining coherent reasoning across long contexts.
Anthropic has published significant research on mechanistic interpretability—understanding the internal workings of neural networks—and techniques for reducing model hallucinations. Their innovations tend to prioritize safety and reliability over raw capabilities, though Claude models have demonstrated competitive performance on many benchmarks.
Ethical Standards and AI Safety
OpenAI has developed a multi-layered approach to AI safety and ethics. Their Preparedness Framework outlines how they assess and mitigate risks from increasingly capable AI systems. They employ red-teaming exercises, where specialized teams attempt to make models produce harmful outputs, to identify and address vulnerabilities before deployment.
The organization has published research on AI alignment techniques and established a superalignment team focused on ensuring future superintelligent systems remain aligned with human values. However, some critics argue that OpenAI’s commercial interests sometimes conflict with their safety objectives, pointing to instances where models were released despite known limitations.
Anthropic has made ethical AI development their core mission, with safety considerations integrated into every aspect of their research and product development. Their constitutional AI approach embeds ethical principles directly into model training, creating systems that can reflect on and revise their own outputs based on these principles.
Anthropic regularly publishes detailed safety research and has been transparent about the limitations of their models. Their “Core Views on AI Safety” document outlines their perspective on risks from advanced AI and their approach to addressing these challenges. This safety-first stance has earned them credibility among AI safety researchers, though some argue it may constrain their commercial competitiveness.
“The fundamental question isn’t whether AI systems can be made safe in principle—it’s whether we’ll put in the work to make them safe in practice before deploying increasingly powerful systems.”
Financial Backing and Investment Strategy
OpenAI has secured massive financial backing, most notably through a multi-year, $10 billion investment from Microsoft. This partnership gives Microsoft exclusive access to certain OpenAI technologies while providing OpenAI with the computing resources needed for training advanced models. Additional investors include Khosla Ventures, Reid Hoffman, and other prominent technology figures.
Their investment strategy has prioritized computational infrastructure, talent acquisition, and product development. The shift from a non-profit to a “capped-profit” model was explicitly designed to attract the capital necessary for competing in increasingly expensive AI research while maintaining alignment with their mission.
Anthropic has raised over $4 billion in funding, with major investments from Google, Amazon, and Salesforce. Google’s $300 million investment came with a 10% stake in the company, while Amazon committed up to $4 billion with plans to integrate Claude into AWS services. Other investors include Spark Capital, Jaan Tallinn (Skype co-founder), and Dustin Moskovitz (Facebook co-founder).
Anthropic’s investment strategy emphasizes long-term research on AI safety and alignment, though they have increasingly allocated resources to product development and go-to-market efforts. Their funding approach has sought to maintain independence while securing the resources needed for competitive AI development.
OpenAI Funding
- $10B from Microsoft (multi-year commitment)
- Earlier rounds from Khosla Ventures, Reid Hoffman
- Reported valuation of $80-90 billion
- Revenue estimated at $1.6B+ annually (2023)
Anthropic Funding
- Up to $4B from Amazon (multi-year commitment)
- $300M from Google (10% stake)
- $450M from Spark Capital, others
- Reported valuation of $15-20 billion
Reputation and Industry Perception
OpenAI enjoys widespread brand recognition, with ChatGPT becoming virtually synonymous with generative AI in the public consciousness. Their models are widely used by developers and enterprises, and their research has significantly influenced the direction of the AI field. However, their reputation has evolved over time, with some critics noting a shift from their original open-source ethos toward a more commercial orientation.
Within the AI research community, OpenAI is respected for technical achievements but has faced criticism for reducing the transparency of their research and for releasing models with known limitations. The November 2023 board crisis that temporarily removed and then reinstated CEO Sam Altman raised questions about governance and internal alignment.
Anthropic has cultivated a reputation for thoughtful, safety-oriented AI development. They are particularly well-regarded within the AI alignment and safety research communities, where their technical publications and constitutional AI approach have earned respect. Their more cautious deployment strategy has resonated with enterprises concerned about AI risks.
As a younger company, Anthropic has lower public awareness than OpenAI but has built strong credibility with technical audiences and enterprise customers. Their leadership team’s background in AI safety research lends authenticity to their safety-first positioning, though some industry observers question whether their approach can scale commercially.
How do developers perceive OpenAI vs Anthropic?
Developers generally view OpenAI as offering more versatile tools with broader capabilities, particularly for multimodal applications. Their extensive documentation and large user community are seen as advantages. Anthropic is perceived as providing more reliable and predictable models with better handling of nuanced instructions and longer contexts, making them preferred for certain enterprise applications where safety and reliability are paramount.
How do academic researchers view the two companies?
Academic researchers tend to appreciate Anthropic’s continued commitment to publishing detailed technical papers and their focus on interpretability research. OpenAI’s earlier research contributions are highly cited, though some researchers have expressed concern about their reduced transparency in recent years. Both organizations employ respected researchers and contribute to the field, but with different emphases and publication strategies.
Global Strategy and Collaborations
OpenAI has pursued global expansion through strategic partnerships and policy engagement. Their collaboration with Microsoft has facilitated international growth, with ChatGPT and API services available in numerous countries. They have engaged with policymakers in the United States, European Union, and other jurisdictions to shape AI governance frameworks.
Their approach to international markets has balanced growth with regulatory compliance, adapting to regional requirements while maintaining consistent core capabilities. OpenAI has established offices in multiple countries and participated in global AI standards development through organizations like the Partnership on AI.
Anthropic has taken a more measured approach to global expansion, focusing on research collaborations and selective international partnerships. They have engaged with AI safety organizations globally and contributed to international discussions on AI governance. Their Claude assistant is available in a growing number of countries, though with a more limited footprint than OpenAI’s offerings.
Both companies navigate complex geopolitical considerations as AI becomes increasingly viewed as a strategic technology. Their global strategies reflect different priorities—OpenAI’s broader commercial reach versus Anthropic’s emphasis on research partnerships and safety-oriented collaborations.
North America
- OpenAI: HQ in San Francisco, Microsoft partnership
- Anthropic: HQ in San Francisco, Amazon/Google partnerships
- Both: Active in US AI policy discussions
Europe
- OpenAI: London office, EU AI Act engagement
- Anthropic: Research collaborations with European institutions
- Both: Adapting to EU AI regulations
Asia-Pacific
- OpenAI: Partnerships in Japan, Australia
- Anthropic: Selective enterprise partnerships
- Both: Navigating complex regulatory landscape
Challenges and Future Trajectories
OpenAI faces several significant challenges as it advances toward more capable AI systems. The computational requirements for training cutting-edge models continue to escalate, demanding massive infrastructure investments. Governance questions persist about how to manage increasingly powerful systems while balancing commercial interests with their mission of beneficial AGI.
Their future trajectory likely involves continued scaling of models, expansion of multimodal capabilities, and deeper integration with Microsoft’s ecosystem. OpenAI has indicated interest in developing more agentic AI systems that can perform complex tasks autonomously, raising both opportunities and safety considerations.
Anthropic confronts the challenge of scaling their safety-focused approach while remaining competitive in a fast-moving field. They must demonstrate that their constitutional AI methodology can extend to increasingly capable systems without compromising performance. As a younger company, they also face the task of expanding their market presence while maintaining their principles.
Looking ahead, Anthropic will likely continue emphasizing interpretability research and safety techniques while gradually broadening their product offerings. Their partnership with Amazon suggests a strategic focus on enterprise AI applications, particularly in regulated industries where their safety emphasis provides competitive differentiation.
Key Future Considerations for Both Companies
- Navigating evolving AI regulations across global markets
- Managing compute resources and environmental impact
- Addressing concerns about AI’s impact on labor markets
- Developing effective governance for increasingly autonomous systems
- Balancing open research with competitive and safety considerations
Conclusion: The Path Forward

The comparison between OpenAI and Anthropic reveals not just a competition between companies, but a dialogue about how advanced AI should be developed and deployed. OpenAI’s approach emphasizes capabilities and scale, pushing the boundaries of what AI can accomplish while implementing safety measures. Anthropic prioritizes safety and alignment from the ground up, developing techniques to make AI systems more reliable and aligned with human values.
Rather than declaring a singular “leader,” it may be more accurate to recognize that both approaches contribute valuable perspectives to the advancement of artificial intelligence. OpenAI’s scale and commercial reach have accelerated AI adoption and demonstrated the technology’s potential, while Anthropic’s safety-first methodology has advanced our understanding of how to make AI systems more reliable and aligned.
The future of AI will likely benefit from this diversity of approaches. As these technologies become increasingly powerful and integrated into society, both innovation and safety will be essential considerations. Organizations that can effectively balance these priorities—whether through collaboration, competition, or a combination of approaches—will shape the next generation of artificial intelligence.
For decision-makers navigating this landscape, understanding the distinct philosophies, strengths, and limitations of companies like OpenAI and Anthropic is crucial for making informed strategic choices about AI adoption and development. The question of leadership in next-generation AI may ultimately depend less on which single company prevails and more on how the field as a whole integrates lessons from different approaches to create beneficial, safe, and powerful AI systems.